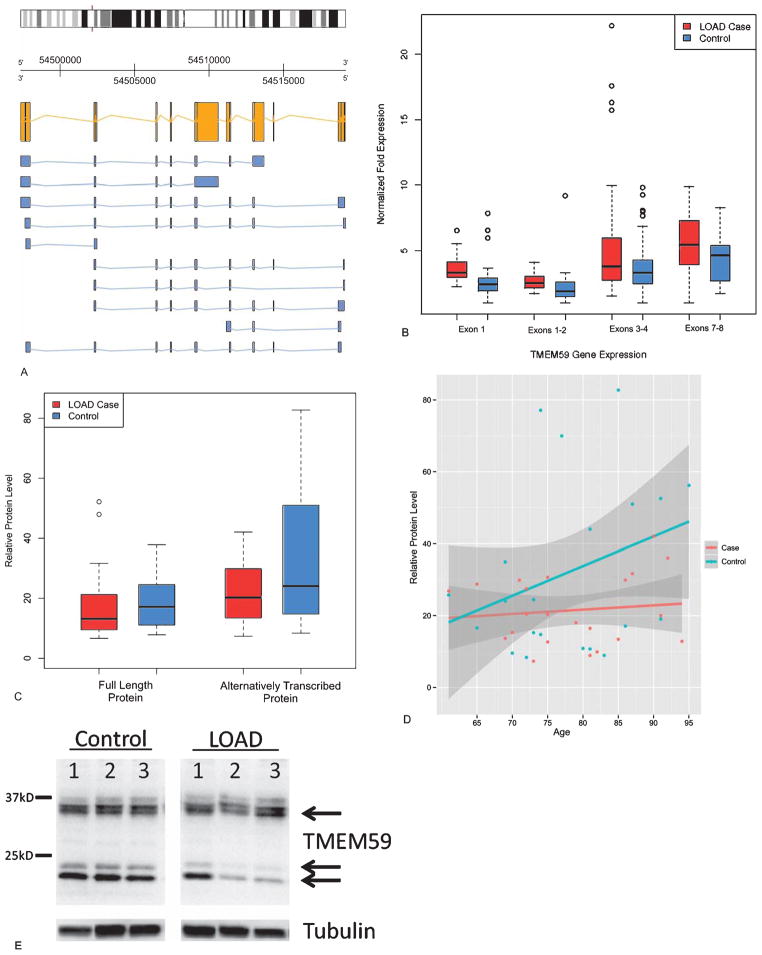
Fig. 6.
Functional validation of observed DNA methylation differences for TMEM59, a gene involved in the post-translational modification of AβPP. A) TMEM59 is located on chromosome 1 and is transcribed on the reverse strand. The reference sequence mRNA is yellow. Predicted alternative isoforms are in blue. B) Boxplot of TMEM59 gene expression by Q-PCR in the Discovery Set. Two-sample t-test between cases and controls were all statistically significant (exon 1 p = 0.0013; exons 1–2 p = 0.0071; exons 3–4 p = 0.0036, exons 7–8 p = 0.0083). C) Boxplot of relative protein levels of TMEM59 in the Discovery Set plus an additional 26 validation samples. Paired t-tests did not reflect case specific differences for the full length protein (p = 0.68), while the shorter protein fragment was significantly lower in AD cases (p = 0.040). D) Levels of the shorter TMEM59 protein fragment as a function of age. E) Representative western blot image of TMEM59 protein expression in controls and AD cases 1–3 representing identical exposures of the same gel. No differences were detected between AD and controls for full length TMEM59 protein based on case status, but the levels of the TMEM59 shorter proteins were reduced in AD cases. These shorter proteins were also observed in the TMEM59 control protein lysate.