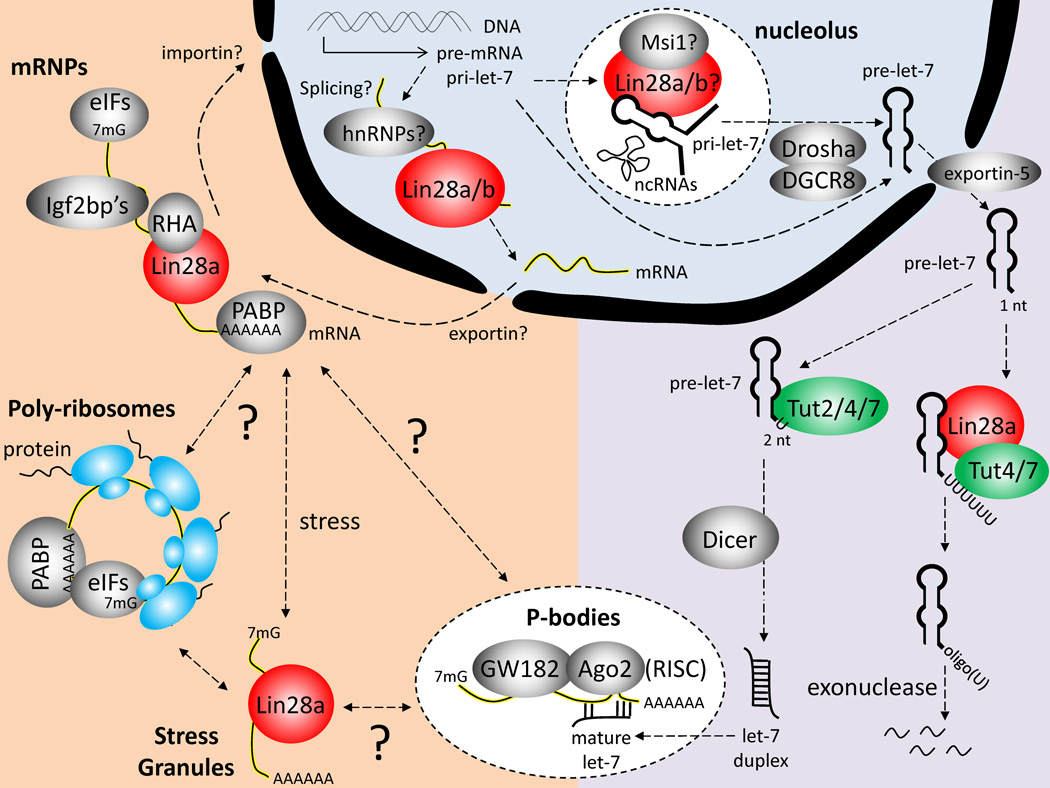
Figure 1. Overview of Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Lin28 Function.
Both Lin28a and Lin28b have been observed to shuttle between the nucleus and cytoplasm, binding both mRNAs and pri-/prelet-7. In the nucleus, Lin28a/b could potentially work in tandem with the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) to regulate splicing, or with Musashi-1 (Msi1) to block pri-let-7 processing. In the cytoplasm, Lin28a recruits Tut4/7 to oligouridylate pre-let-7, and block Dicer processing to mature let-7 miRNA (right, violet). Lin28a also recruits RNA helicase A (RHA) to regulate mRNA processing in messenger ribonucleoprotein (mRNP) complexes, in tandem with the Igf2bp’s, poly(A)-binding protein (PABP), and the eukaryotic translation initiation factors (eIFs). In response to unknown signals and stimuli, the mRNAs are either shuttled into poly-ribosomes for translation, stress granules for temporary sequestering, or P-bodies for degradation, in part via miRNAs and the Ago2 endonuclease (left, orange).