Abstract
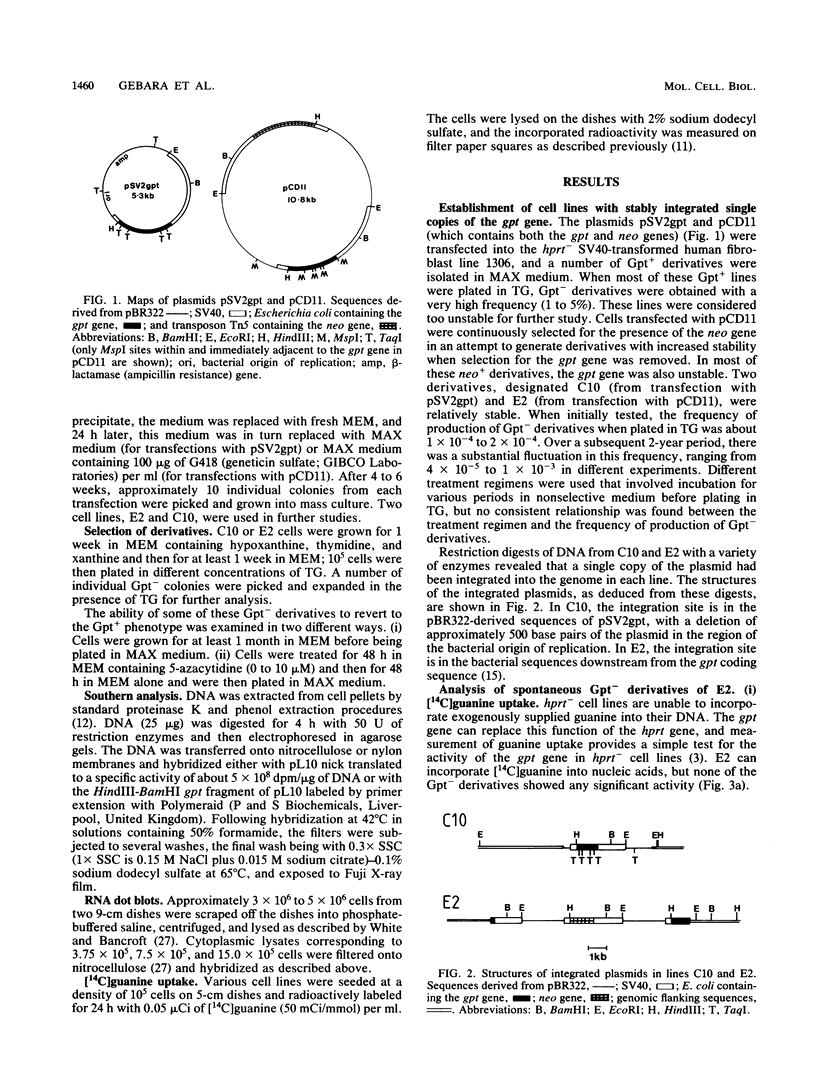
Plasmids containing the bacterial gpt gene under control of the simian virus 40 promoter were transfected into a simian virus 40-transformed human fibroblast line. Two transfectants, E2 and C10, which contain stably integrated single copies of the gpt gene, were isolated. These two lines produce Gpt- variants spontaneously with a frequency of about 10(-4). We carried out a detailed molecular analysis of the spectrum of alterations which gave rise to the Gpt- phenotype in these variants. DNA from 14 of 19 Gpt- derivatives of one of the cell lines (E2) contains deletions or rearrangements of gpt-containing sequences. In four of the remaining five lines, the Gpt- phenotype was correlated with reduced levels of expression rather than with changes in the gross structure of the gpt gene, and it was possible to reactivate the gpt gene. In one Gpt- line, gpt mRNA was present at normal levels, but no active enzyme was produced. Spontaneous Gpt- derivatives of the other cell line (C10) produced a completely different spectrum of alterations. Very few deletions were found, but several derivatives contained additional extrachromosomal gpt sequences, and, remarkably, in two other Gpt- lines, gpt-containing sequences were amplified more than 100-fold. The phenotypes of the majority of the Gpt- derivatives of C10 could be attributed to alterations in gene expression caused by methylation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botchan M., Stringer J., Mitchison T., Sambrook J. Integration and excision of SV40 DNA from the chromosome of a transformed cell. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90242-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R., Stretch A., Thacker J. The nature of mutants induced by ionizing radiation in cultured hamster cells. II. Antigenic response and reverse mutation of HPRT-deficient mutants induced by gamma-rays or ethyl methanesulphonate. Mutat Res. 1986 Apr;160(2):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(86)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. F., Green M. H., Lowe J. E. Transient assay, by [3H]guanine incorporation of Escherichia coli xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (GPT) in transfected human fibroblasts. Gene. 1985;40(1):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B., Scangos G. Expression of transferred thymidine kinase genes is controlled by methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6299–6303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough D. W., Kunkel L. M., Davidson R. L. 5-Azacytidine-induced reactivation of a herpes simplex thymidine kinase gene. Science. 1982 Apr 2;216(4541):70–73. doi: 10.1126/science.6175023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. L., Fuhrer-Krusi S., Kucherlapati R. S. Modulation of transfected gene expression mediated by changes in chromatin structure. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90308-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick R. G., Jr, Fuscoe J. C., Caskey C. T. Amplification versus mutation as a mechanism for reversion of an HGPRT mutation. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Jan;10(1):71–84. doi: 10.1007/BF01534474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly D. J., Willis R. C., Friedmann T. Variable stability of a selectable provirus after retroviral vector gene transfer into human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1141–1147. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A. Altering gene expression with 5-azacytidine. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):485–486. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90192-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann A. R., Kirk-Bell S., Mayne L. Abnormal kinetics of DNA synthesis in ultraviolet light-irradiated cells from patients with Cockayne's syndrome. Cancer Res. 1979 Oct;39(10):4237–4241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrander M., Vogel S., Silverstein S. Phenotypic switching in cells transformed with the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):708–714. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt D., Subramani S. Nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8817–8823. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Jones P. A. 5-methylcytosine, gene regulation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1983;40:1–30. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60678-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. M., Axel R. Gene amplification and gene correction in somatic cells. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roginski R. S., Skoultchi A. I., Henthorn P., Smithies O., Hsiung N., Kucherlapati R. Coordinate modulation of transfected HSV thymidine kinase and human globin genes. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90217-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in cultured animal cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stankowski L. F., Jr, Tindall K. R., Hsie A. W. Quantitative and molecular analyses of ethyl methanesulfonate- and ICR 191-induced mutation in AS52 cells. Mutat Res. 1986 Apr;160(2):133–147. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(86)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacker J., Debenham P. G., Stretch A., Webb M. B. The use of a cloned bacterial gene to study mutation in mammalian cells. Mutat Res. 1983 Sep;111(1):9–23. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(83)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tindall K. R., Stankowski L. F., Jr, Machanoff R., Hsie A. W. Analyses of mutation in pSV2gpt-transformed CHO cells. Mutat Res. 1986 Apr;160(2):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(86)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tindall K. R., Stankowski L. F., Jr, Machanoff R., Hsie A. W. Detection of deletion mutations in pSV2gpt-transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1411–1415. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. R., Morley A. A., Haliandros M., Kutlaca R., Sanderson B. J. In vivo somatic mutations in human lymphocytes frequently result from major gene alterations. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):343–345. doi: 10.1038/315343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
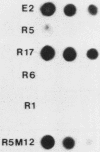
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]