Fig. 3.
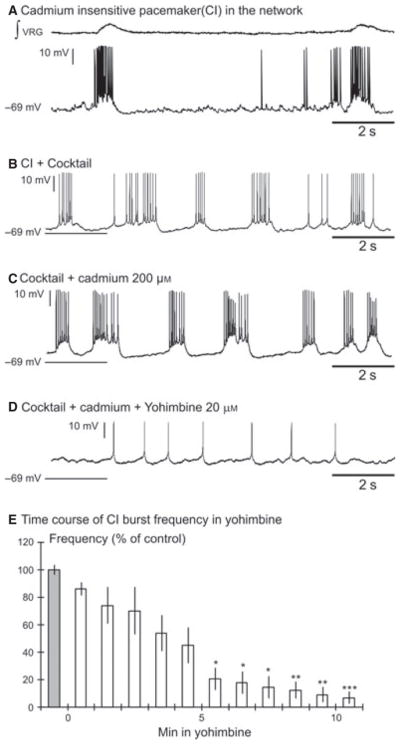
Yohimbine abolished the burst properties of CI inspiratory pacemaker neurons. (A) Recording of an inspiratory pacemaker neuron in the network. (B) This neuron continued to burst after blockade of the fast synaptic transmission by the cocktail and (C) after application of cadmium. (D) Yohimbine (20 μM) abolished the burst properties of the CI pacemaker neuron. (E) The histogram represents the time course of the burst frequency of synaptically isolated CI pacemaker neurons (n = 8) during a 10-min bath application of yohimbine. Each bin represents the burst frequency for a time window of 1 min. The percentage of control frequency was calculated based on the mean frequency 1 min before bath application of yohimbine (grey bin); ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, Friedman test. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM.
