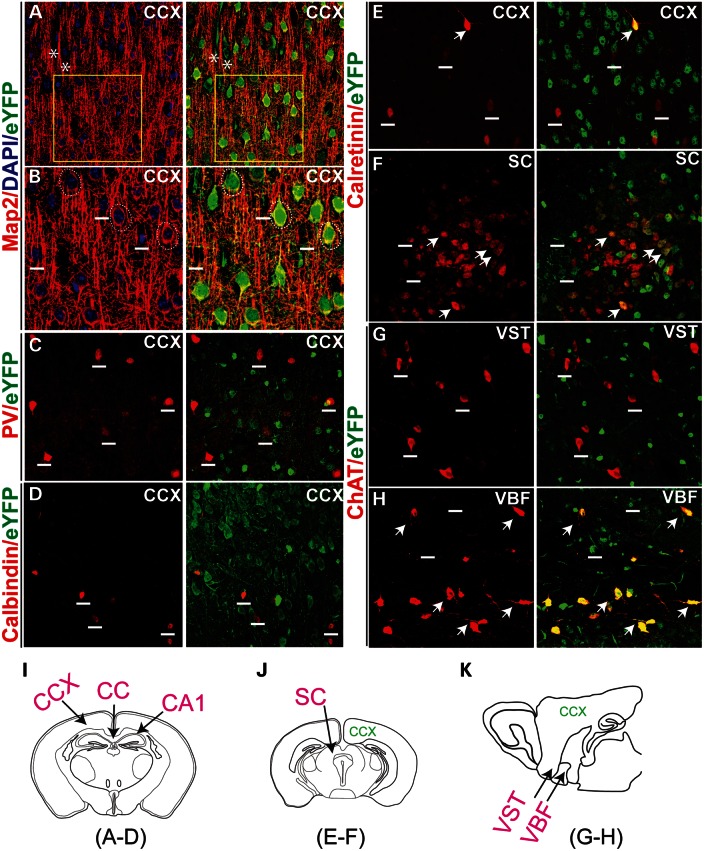
Figure 3.
Description of Pk1-expressing neurons in the brain. (A) Pk1 expression overlaps with Map2, a neuronal maker that labels all pyramidal neurons in the cortex (red). Asterisks indicate two Map2 negative glia cells expressing Pk1 gene (eYFP, green). Boxed areas are zoomed in (B). (B) Pk1 colocalizes with soma staining of Map2 enclosing the neurons’ nuclei indicated by dashed circles. Neurons negative for Map2 do not express Pk1 (above the short lines). (C–E) A majority of PV (C), calbindin (D) and calretinin (E)-stained interneurons in the cortex do not express Pk1 (eYFP). Short lines indicate interneurons expressing the calcium-binding proteins, but not eYFP. (F) In the SC, a few more calretinin neurons express a low level of Pk1 as indicated by arrows. (G) Cholinergic neurons that are labeled with ChAT (red) in the VST do not express Pk1 (short lines in G). (H) ChAT neurons in VBF coexpress Pk1 (arrows in H). (I–K) Schematic illustrations of sections of imaged areas for the relevant panels that are indicated below the diagram.