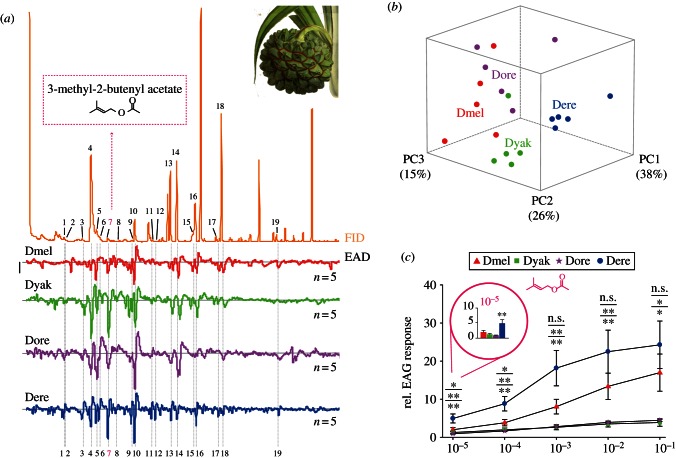
Figure 2.
Antennal response spectra of the four melanogaster sibling species—evoked by the Pandanus sp. fruit headspace volatiles. (a) Headspace odour of Pandanus sp. fruits (upper part) and EAD responses (lower part). Bar stands for 1 mV of EAD response. Active compounds are coded as follows: 2,3-butanediol (no. 1), ethyl butyrate (no. 2), ethyl isovalerate (no. 3), isoamyl acetate (no. 4), 2-heptanone (no. 5), styrene (no. 6), 3M2BA (no. 7), ethyl tiglate (no. 8), 6-methyl-5-heptene-2one (no. 9), ethyl hexanoate (no. 10), linalool (no. 13), phenethyl alcohol (no. 14), benzyl acetate (no. 15), ethyl benzoate (no. 16), isopentyl hexanoate (no. 17), β-phenethyl acetate (no. 18). Peaks (no. 11), (no. 12) and (no. 19) are unidentified. Emphasized in pink is the novel Drosophila ligand 3M2BA (no. 7). (b) PCA (variance–covariance matrix) of quantified GC-EAD responses. PC1, 2 and 3 are plotted in three-dimensional space (79% cumulative variance). Species differ significantly from each other (one-way ANOSIM; Bray–Curtis distance; R = 0.78; p < 0.001). Isoamyl acetate (no. 4), 3M2BA (no. 7) and phenethyl alcohol (no. 14) most supported to the observed dissimilarity (SIMPER; all groups pooled; cumulative contribution 30.8%). (c) EAG dose–response curves of 3M2BA from the four species. Drosophila erecta is highly sensitive to 3M2BA, starting at 10−5 (paired t-test, **p < 0.01, emphasized). Drosophila erecta differs from its siblings (one-way ANOVA; Turkey's post hoc test; p > 0.05 n.s.; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). Mean ± s.e. In all graphs, species abbreviation and colour-code is as follows: D. melanogaster (Dmel, red), D. yakuba (Dyak, green), D. orena (Dore, violet) and D. erecta (Dere, blue), and n = 5 per species. Pandanus candelabrum image adapted from an original illustration. Reproduced with the kind permission of the Director and the Board of Trustees, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.