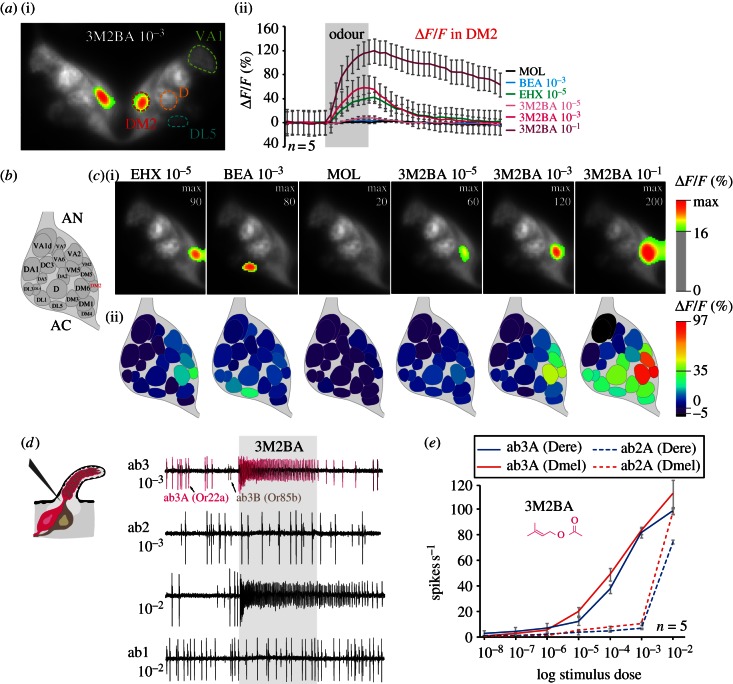
Figure 3.
Identification of ORs activated by 3-methyl-2-butenyl acetate via functional imaging and single sensillum recordings. (a) Functional imaging in D. melanogaster. Representative recording of both ALs performed with 3M2BA (i), and activity traces of the DM2 glomerulus (ii) in response to the same set of odours as used in (c). Error bars represent s.d. (b) Glomerular atlas of the AL. (c) Representative recordings performed with different reference stimuli (EHX, ethyl hexanoate; BEA, benzaldehyde; and MOL, mineral oil) and different 3M2BA concentrations illustrate the strong activation of DM2 glomerulus by 3M2BA (i). Images are individually scaled to the strongest activated glomeruli. Values below the ΔF/F threshold are omitted to illustrate the specificity of the signals, as well as the glomerular arrangement as visualized by the intrinsic fluorescence. Corresponding odour-induced activity (average % ΔF/F) plotted on schematic ALs (ii). (d) Single sensillum recording (SSR) measurements of the large basiconic sensilla in female D. erecta illustrate strong activation of the Or22a receptor (ab3A neuron) by 3M2BA. At higher concentrations, Or59b (ab2A neuron) is also activated. (e) SSR dose–response experiments performed on ab2 and ab3 sensilla in D. erecta (blue: solid line, ab3A Dere; dashed line, ab2A Dere) and D. melanogaster (red: solid line, ab3A Dmel; dashed line, ab2A Dmel) females with 3M2BA. Mean ± s.e.