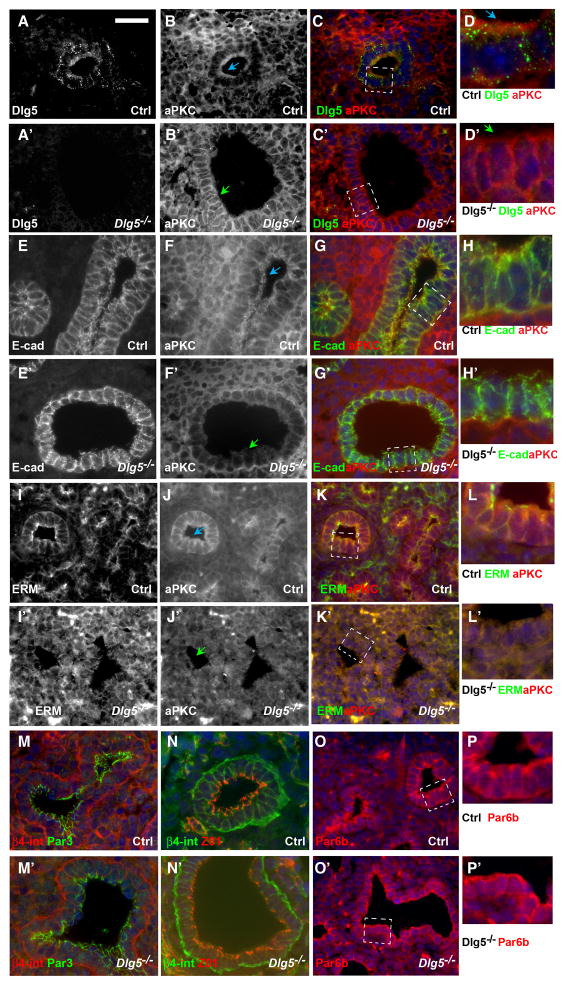
Figure 5. Dlg5 is required for apical localization of atypical PKC (aPKC) and maintenance of apical-basal cell polarity.
(A–D′) Immunofluorescent stainings of lung sections from E14.5 wild-type (Ctrl) and Dlg5−/− embryos with anti-Dlg5 (A–A′, green in C–D′) and anti-aPKC (B–B′, red in C–D′) antibodies. Note partial co-localization of Dlg5 and aPKC in control cells (A–D) and loss of apical and prominent lateral membrane staining of aPKC in Dlg5 −/− cells (B′, D′).
(E–P′) Immunofluorescent stainings of lung sections from E14.5 wild-type (Ctrl) and Dlg5−/− embryos with anti-E-cadherin (E–E′, green in G–G′, H–H′), anti-aPKC (F–F′, J–J′, red in G–G′, H–H′, K–K′, L–L′), anti-ERM (I–I′, green in K–K′, L–L′), anti-Par3 (green in M–M′), anti-β4-integrin (red in M–M′, green in N–N′), anti-ZO1 (red in N–N′) and anti-Par6b (red in O–P′) antibodies. Note properly polarized localization of basal (β4-integrin), apical (Par6b, Par3) and tight junctional (ZO1) markers in E14.5 Dlg5 −/− cells. Areas in dashed white boxes in C–C′, G–G′, K–K′, O–O′ are shown at higher magnification in D–D′, H–H′, L–L′, P–P′, respectively.
Blue arrows denote properly localized apical aPKC and green arrows denote loss of apical aPKC in Dlg5 −/− cells.
Bar in A represents 67 μm in A–C′, E–G′, I–K′, M–O′, 20 μm in D–D′, H–H′, L–L′, P–P′.