Figure 3.
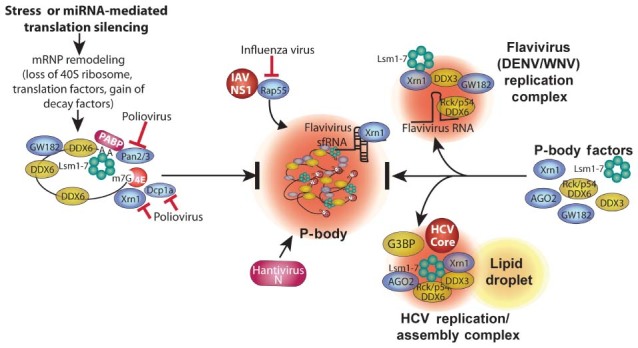
Pathways of PB disruption by viruses. PBs form via a complex series of events involving remodeling mRNPs by stripping of initiation factors and ribosome subunits, association with GW182, undergoing Pan2/3‐mediated deadenylation,microtubule transport, and association with other RNA decay factors (e.g., Xrn1, Dcp1a, DDX6 (Rck/p54), GW182 and Lsm components of the exosome), and final concentration in P‐bodies. The order of association of factors with mRNPs in PBs is arbitrary. HCV subverts many PB components into novel viral replication/assembly foci with viral core protein that also contain some SG components (e.g., G3BP, Figure 2). Flaviviruses also divert PB factors into replication foci, likely bound with viral RNA through interaction with DDX6(Rck/p54). Poliovirus induces cleavage of Dcp1a and rapid degradation of Xrn1 and Pan3. Rap55 is a critical PB factor that IAV protein NS1 diverts from normal association with PBs. Bunyavirus Junin virus incorporates viral N protein into PBs to interfere with cellular Dcp1a/2 decapping function and facilitate viral cap‐snatching.
