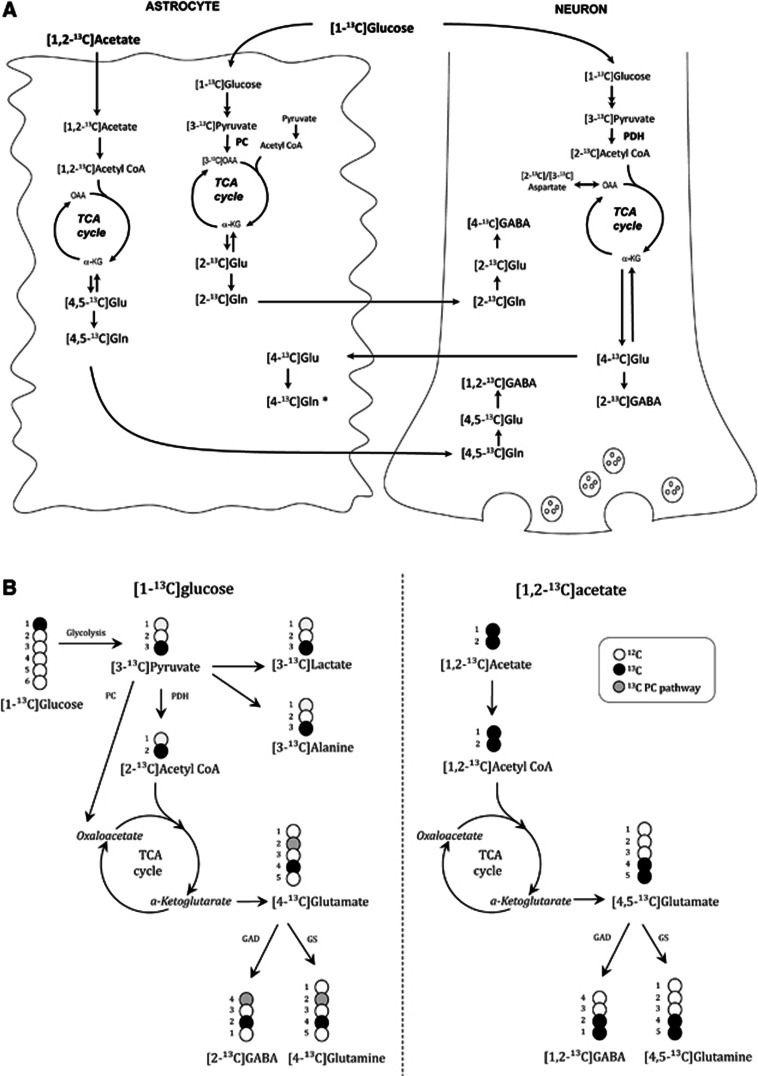
Figure 1.
(A) A simplified overview of a selection of 13C labeling patterns originating from pathways of metabolism of [1-13C]glucose and [1,2-13C]acetate. For simplicity, a hypothetical pluripotent neuron is represented that is both glutamatergic and GABAergic. [1-13C]Glucose is converted to [3-13C]pyruvate via glycolysis, and [3-13C]pyruvate can be decarboxylated to [2-13C]acetyl CoA and subsequently enter the TCA cycle. After several steps, [4-13C]α-KG is formed and is precursor for [4-13C]glutamate, which can subsequently be converted to [2-13C]GABA in GABAergic neurons. When [4-13C]glutamate is released during neurotransmission, astrocytes take up [4-13C]glutamate from the synaptic cleft and convert it to [4-13C]glutamine. In astrocytes, [3-13C]pyruvate originating from [1-13C]glucose can also be converted to [3-13C]OAA by the action of pyruvate carboxylase and give rise to [2-13C]glutamate after several steps. This can be converted to [2-13C]glutamine and sent to neurons for conversion to [2-13C]glutamate and to [4-13C]GABA in GABAergic neurons. [1,2-13C]Acetate is converted to [1,2-13C]acetyl CoA in astrocytes. Following entry into the TCA cycle, [4,5-13C]α-KG is formed after several steps, and is the precursor for [4,5-13C]glutamate and [4,5-13C]glutamine. After transfer of [4,5-13C]glutamine to the neuronal compartment, it is reconverted to [4,5-13C]glutamate in glutamatergic neurons and further to [1,2-13C]GABA in GABAergic neurons. *It should be noted that [4-13C]glutamine can be synthesised from [1-13C]glucose in astrocytes as well, but this is omitted from the figure for simplicity. (B) Schematic representation of glutamate, glutamine and GABA isotopomers derived from [1-13C]glucose and [1,2-13C]acetate. Black circles represent 13C labeling, white circles represent 12C, and gray circles indicates labeling of metabolites from pyruvate carboxylation. For more details, see the Materials and methods section. α-KG, α-ketoglutarate; acetyl CoA, acetyl Coenzyme A; GAD, glutamic acid decarboxylase; Glu, glutamate; Gln, glutamine; GS, glutamine synthetase; OAA, oxaloacetate; PC, pyruvate carboxylase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle.