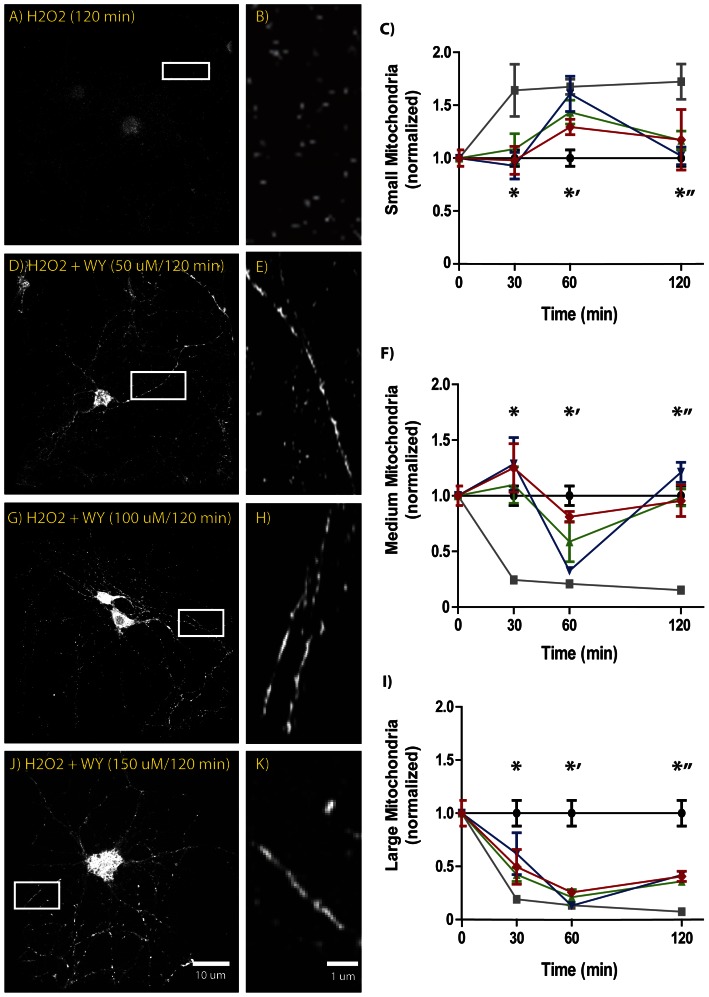
Figure 2. H2O2-induced mitochondrial size decrease is prevented by WY pre-treatment in hippocampal neurons.
A, D, G, J microphotographs of mitochondrial population under different experimental conditions. B, E, H, K: image enlargement to show variations in mitochondrial morphology observed under different experimental conditions. C, F, I: Normalized mitochondrial size quantification (black: control; gray: H2O2; green: 50 µM WY+H2O2; blue: 100 µM WY+H2O2; red: 150 µM WY+H2O2). C) * indicates statistically significant differences between H2O2 and Control (F 9.275, d.f. 4, C.I. 0.06947 to 0.631, t 4.078, p<0.001); *’ indicates statistically significant differences between H2O2 and Control (F 9.275, d.f. 4, C.I. 0.08051 to 0.6564, t 4.183, p<0.001.), interestingly at 60 min only 100 µM WY shows significant differences respect Control (F 9.275, d.f. 4, C.I. −0.0009977 to 0.6653, t 3.259, p<0.01); *” indicates significant differences between H2O2 and all other treatments (F 9.275, d.f. 4. Control C.I. 0.1069 to 0.6828, t 4.482, p<0.001; 50 µM WY C.I. −0.617 to 0.01, t 3.165, p<0.01; 100 µM WY C.I. −0.7046 to −0.06217, t 3.902, p<0.001; 150µM WY C.I. −0.6306 to 0–0303, t 2.969, p<0.05). F) *, *’ and *” indicate significant differences between H2O2 and Control (F 21.3, d.f. 4. Control: * C.I. −0.3851 to −0.09656, t 5.457, p<0.001; *’ C.I. −0.3995 to −0.1036, t 5.558, p<0.001; *” C.I. −0.4178 to −0.1218, t 5.961, p<0.001). No significant differences were observed between Control and WY concentrations, except for 100 µM WY at 60 min (F 21.3, d.f. 4, C.I. −0.386 to −0.04365, t 4.102, p<0.001). I) At each single time point significant differences were registered between Control and all other experimental conditions; however, at 120 min was possible to observe a different tendency for WY pre-treated curves and that of H2O2.