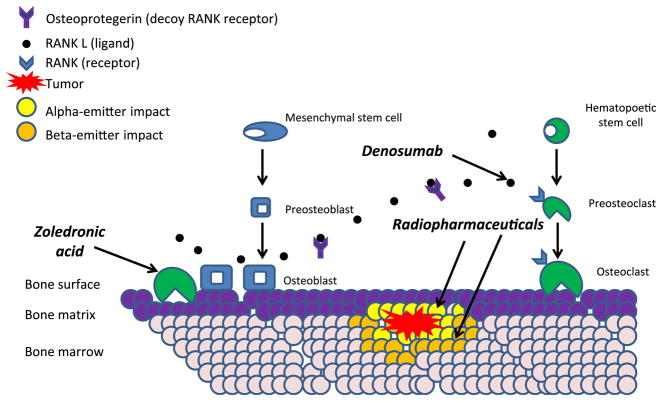
Figure 1.
Simplified schema of bone directed therapies and their primary targets. Osteoblasts produce receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa b ligand (RANKL) which binds to its receptor (RANK) on osteoclast precursors, stimulating osteoclast activity. Regulation of such stimulation is exerted by osteoblast production of osteoprotegerin, a soluble decoy receptor of RANKL. Available treatments utilize these pathways. Denosumab binds to RANKL, preventing it from binding to its receptor on osteoclast precursors. Bisphosphonates prevent osteoclast activity by binding to hydroxyapatite in bone. Radiopharmaceuticals deliver ionized radiation to bone metastases. The impact of alpha and beta emitters on surrounding bone marrow are not drawn to scale.