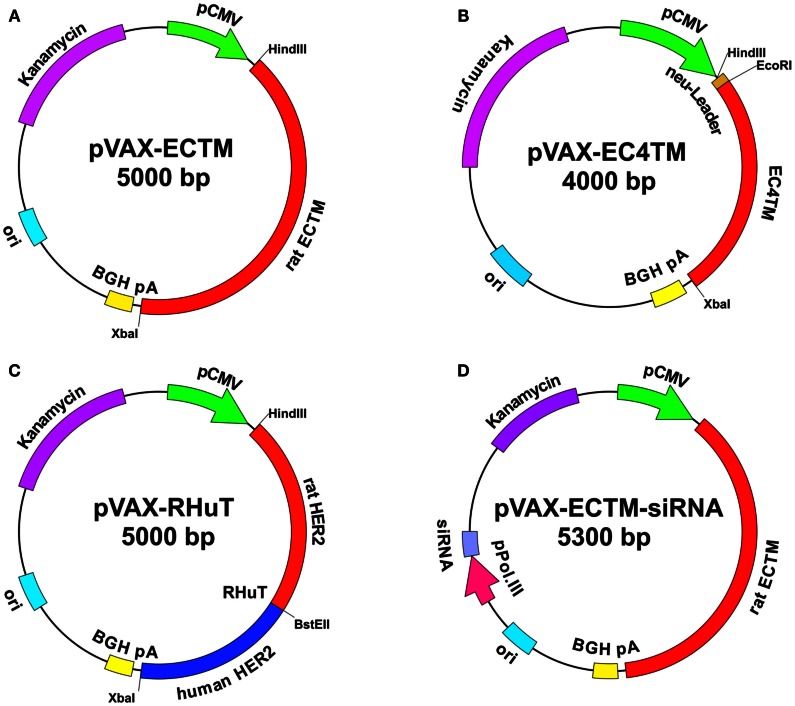
Figure 1.
Maps of anti-HER2 DNA vaccines. pVAX1 (3.0 kb) (Invitrogen) was used as a backbone. The vectors contain the following elements: human cytomegalovirus immediate-early (CMV) promoter (green) for high-level expression in a wide range of mammalian cells; bovine growth hormone (BGH) polyadenylation signal (yellow) for efficient transcription termination and the polyadenylation of mRNA; kanamycin resistance gene (purple) for selection in E. coli; and the origin of bacterial replication (pUC ori, light blue). pVAX-EC-TM (A): the cDNA (about 2 kb) that encodes the extracellular (EC) and transmembrane (TM) domains of rat HER2 was cloned into pVAX1 using HindIII and XbaI restriction enzymes. pVAX-EC4-TM (B): the cDNA that encodes a truncated form of rat HER2, which displays an EC domain that was shortened by 310 NH2-terminal residues and a TM domain, was inserted into pVAX1 using EcoRI and XbaI restriction enzymes, downstream of the leader sequence that had been previously cloned with HindIII and EcoRI. RHuT (C): rat cDNA that encodes the 410 NH2-terminal residues of HER2 was cloned into pVAX1 using HindIII and BstEII restriction enzymes upstream of the human cDNA that encodes the remaining residues of the EC and the TM domains previously cloned using BstEII and XbaI restriction enzymes. pVAX-EC-TM-siRNA (D): a silencing module, which generates a short hairpin (sh)RNA under the control of a polymerase III promoter was inserted into pVAX-EC-TM. The interference cassette is composed of the pH1 or pU6 promoter upstream of an insert that specifies a 19–21-nt sequence derived from the target transcript, separated by a short spacer (6–9 nt) from the reverse complement of the same 19–21 nt sequence.