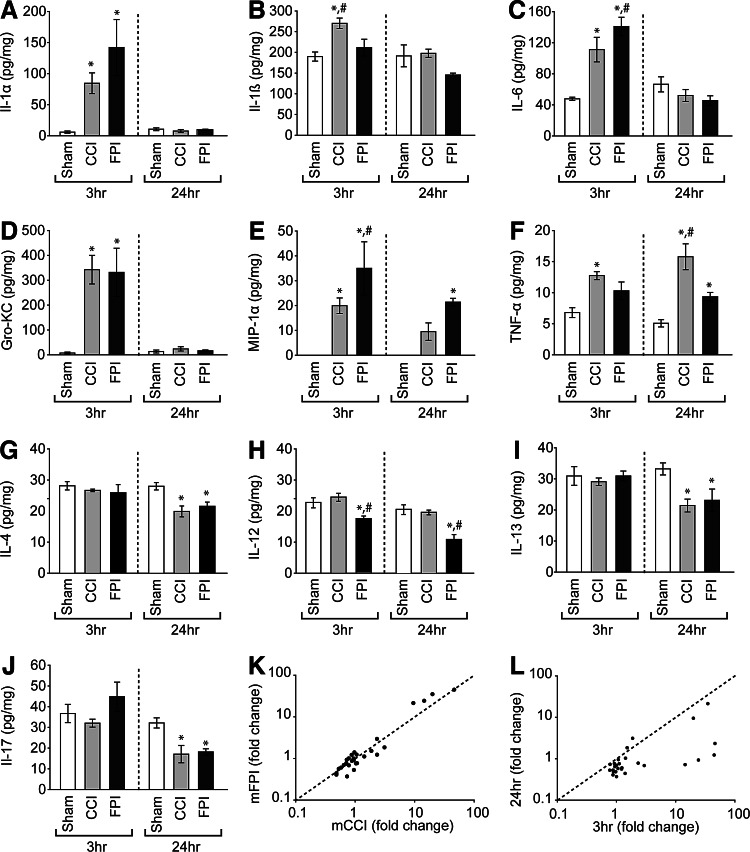
FIG. 6.
Cytokine and chemokine levels detected in cortical tissue extracts at 3 and 24 h post–mild injury. Cortical tissues underlying the site of injury (n=4/model/time point) were harvested, homogenized, and subjected to parallel analysis of the abundance of 23 different cytokine and chemokine targets. Comparisons across groups and time were carried out using two-way ANOVAs. Levels of (A) IL-1α (interaction, F(2,18)=6.10, p=0.009), (B) IL-1β (group main effect: F(2,18)=6.76, p=0.006), (C) IL-6 (interaction, F(2,18)=17.39, p<0.001), (D) Gro-KC (interaction, F(2,18)=8.35, p=0.005), (E) MIP-1α (group main effect: F(2,18)=17.19, p<0.001), and (F) TNF-α (group main effect: F(2,18)=25.35, p<0.001) were significantly up-regulated after mTBI. In contrast, (G) IL-4 (group main effect: F(2,18)=5.54, p=0.013), (H) IL-12 (group main effect: F(2,18)=24.66, p<0.001), (I) IL-13 (group main effect: F(2,18)=4.40, p=0.028), and (J) IL-17 (interaction, F(2,18)=3.2, p=0.044) were found to have levels that were significantly different than those detected in sham-operated animals. Data are presented as mean±standard error of the mean. *Significantly different than sham; #significant difference between mCCI and mFPI. (K) Relationship between fold changes detected in cytokine and chemokine levels across injury types within time. (L) Relationship between fold changes detected in cytokine and chemokine levels across time within injury model. ANOVAs, analyses of variance; IL, interleukin; MIP, macrophage inflammatory protein; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; mTBI, mild traumatic brain injury; mCCI, mild controlled cortical impact; mFPI, mild fluid percussion injury.