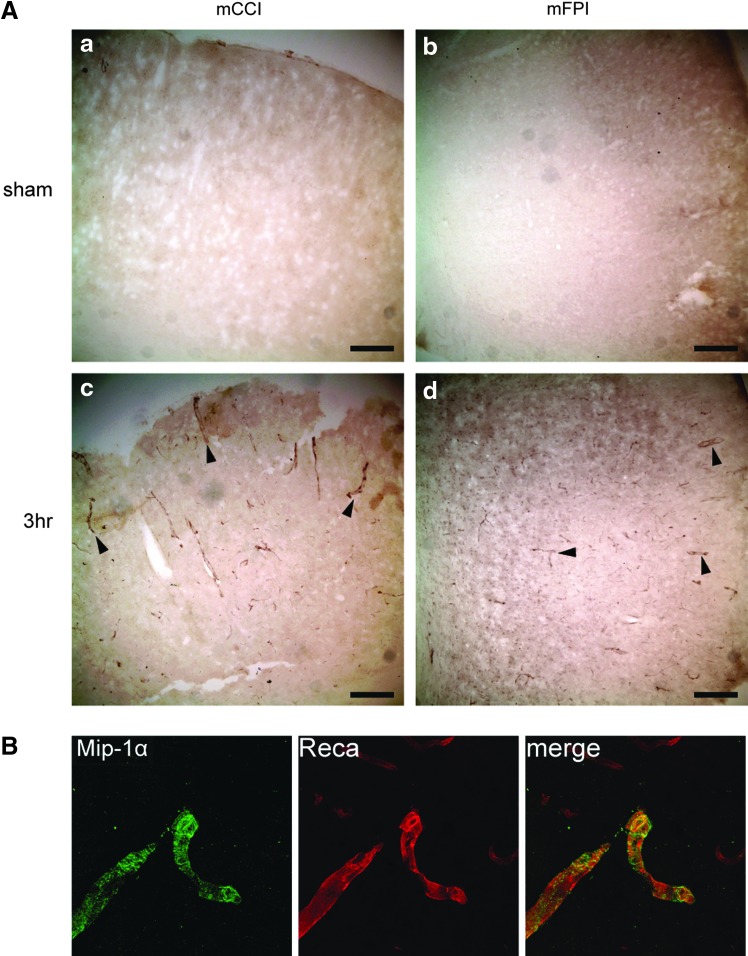
FIG. 8.
Increased Mip-1α immunostaining after mild injury was associated with cortical vasculature. (A) Bright field images taken of sections from mCCI (a and c) and mFPI (b and d) injured animals immunostained with anti-Mip-1α Abs and detected using a biotinylated secondary and visualized with a peroxidase-conjugated tertiary Ab. Sections taken from sham animals showed no detectable signal (a and b). At 3 h (c and d) postinjury, Mip-1α immunoreactivity was observed in vessel-like structures in the cortex underlying the site of injury. Arrowheads, Mip-1α staining; scale bars: 200 μm. (B) Confocal image of the cortex underlying the injury site taken from a 3-h post-mFPI section immunostained for Mip-1α (green) and the endothelial marker, Reca (red). Co-labeling is indicated by yellow color in the merged panel. MIP, macrophage inflammatory protein; mCCI, mild controlled cortical impact; mFPI, mild fluid percussion injury; Abs, antibodies; Reca, rat endothelial cell antigen. Color image is available online at www.liebertpub.com/neu