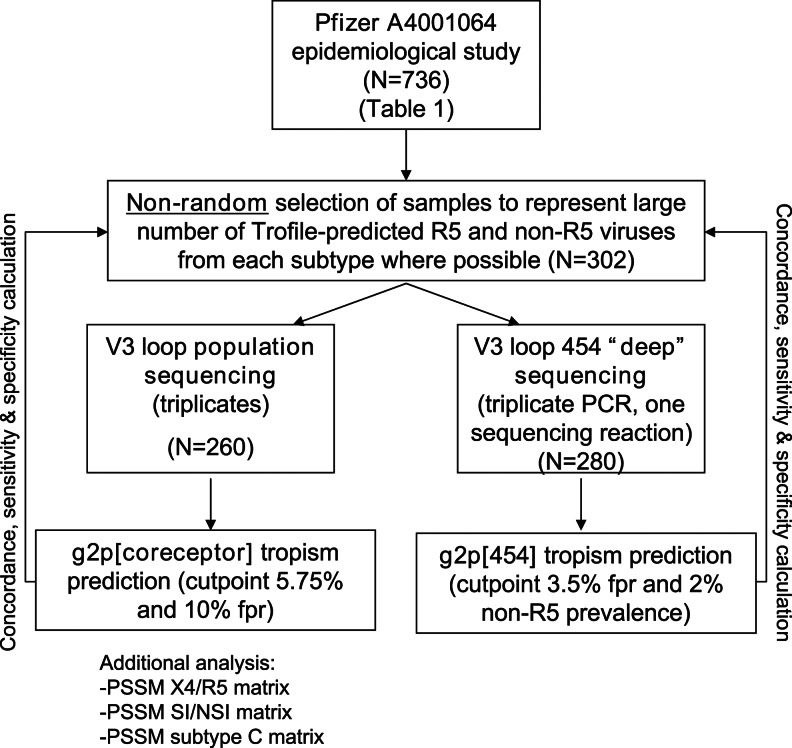
FIG. 1.
Study overview. Samples were selected from the Pfizer A4001064 epidemiologcal study (N=736) to represent a large number of R5 and non-R5 viruses from each subtype (subtype A, N=95, subtype C, N=105, subtype D, N=106). In the population sequencing analysis, subjects who did not yield Trofile results (unblinded only in the analysis stage) and those with only one success in the triplicate sequencing who had R5 viruses were excluded (N=260). V3 sequences from all replicates were fed into g2p[coreceptor], PSSM X4/R5, PSSM SI/NSI, and PSSM subtype C. The worst-case-scenario approach was taken: Among the replicates, the one with the score that predicts the highest likelihood of being non-R5 would be chosen to represent the genotypic tropism of the sample. In the “deep” sequencing portion of the study, first-round polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplicons from the same set of samples and replicates (N=301) underwent “nested” PCR with 454-adapted second-round PCR primers and were put through the 454 “deep” sequencing pipeline. N=280 subjects yielded V3 sequences that successfully passed the g2p[454] alignment and tropism prediction pipeline.