Figure 3.
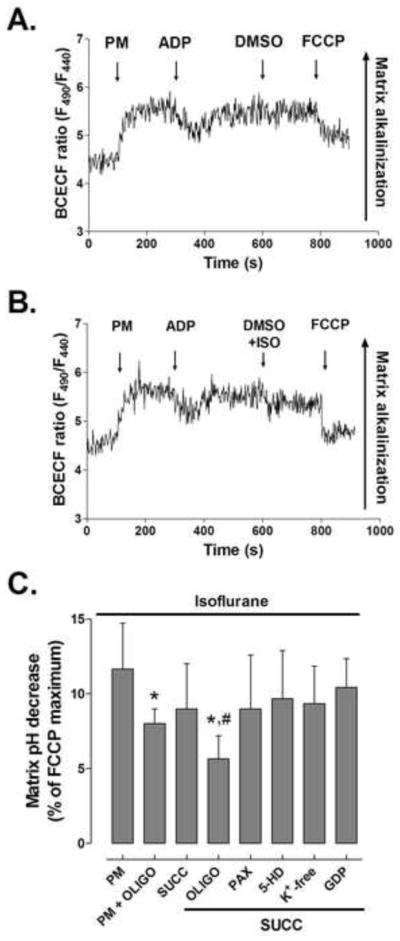
Acidification of mitochondrial matrix by isoflurane. (A) Representative matrix pH trace of BCECF-loaded mitochondria respiring on pyruvate and malate (PM). Addition of substrates raises matrix pH, while ADP induces transient matrix acidification. FCCP abolishes the proton gradient and causes maximal acidification. (B) Isoflurane (ISO) causes a slight decrease in matrix pH. (C) Magnitude of matrix pH decrease relative to FCCP-induced maximum. SUCC = succinate; OLIGO = oligomycin; 5-HD = 5-hydroxydecanoic acid; PAX = paxilline; GDP = guanosine diphosphate. FCCP = carbonylcyanide-p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone. Values are means±S.D., n=5–7, *P<0.05 versus control, #P<0.05 versus PM + OLIGO.
