Figure 1.
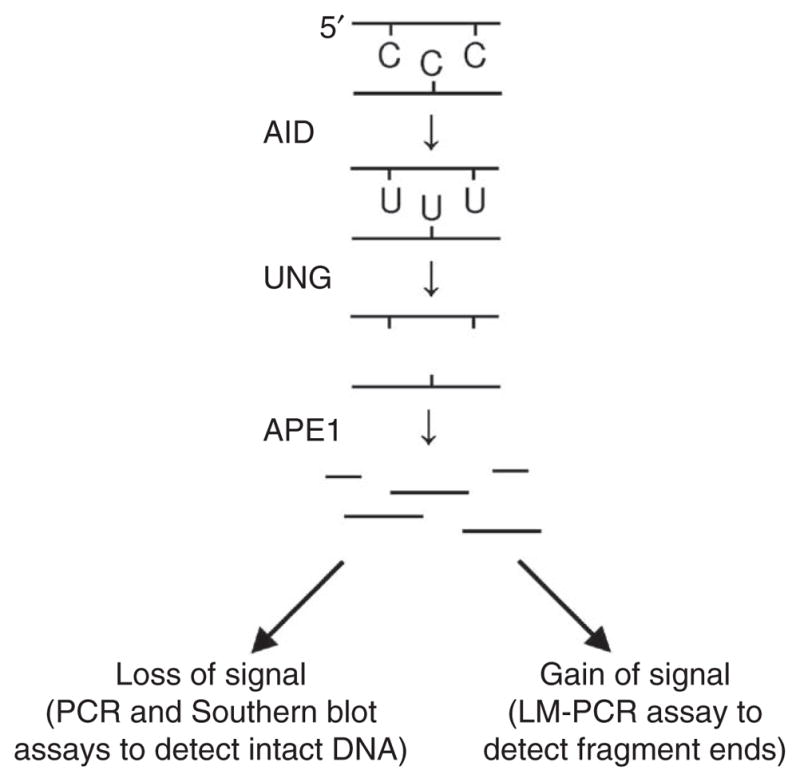
Strategy for identifying uracil residues in DNA. Genomic DNA is isolated from activated Ung−/− B cells and treated with UNG enzyme to remove the uracil bases. The DNA is then digested with APE1 enzyme to convert abasic sites into single-strand breaks. The fragmented DNA is measured in assays that detect either loss of intact DNA or gain of fragment ends. LM-PCR, ligation-mediated PCR.
