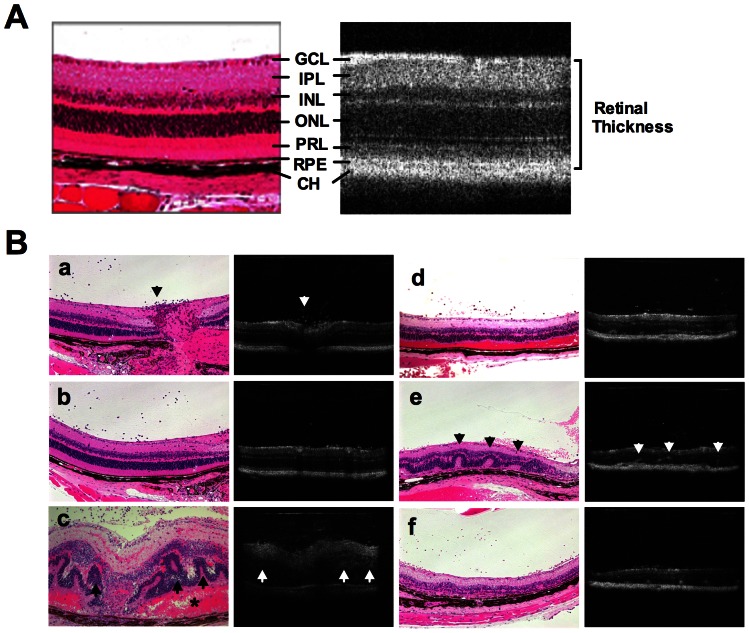
Figure 1. Comparison of OCT images with fundus and histological findings of the retina in EAU.
EAU was induced in B10RIII mice by immunization with 8 ug IRBP in CFA. A, Normal retinal layers in a healthy eye assessed by cross-sectional OCT image in comparison with histological section of murine retina. Note ganglion cell layer (GCL), inner plexiform layer (IPL), inner nuclear layer (INL), outer nuclear layer (ONL), IS/OS of photoreceptor layer (PRL), retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) and choroid (CH). B (a–f), Comparison of cross-sectional OCT images of retina with histological sections of the same eyes at different stages of EAU: a–b, early onset of EAU (13 days post immunization). Note largely normal retinal morphology on OCT and histology, but a moderate degree of cellular infiltrates is apparent in the vitreous near the optic nerve head (arrow); c, acute phase of EAU (14 days post immunization). Note retinal pathology including vitritis, retinal edema, retinal folds (arrow), subretinal hemorrhage (asterisk), retinal and choroidal inflammation. Heavy cellular infiltration in the anterior chamber (not shown) and vitreous limit OCT resolution of retinal layers. In correlation with the pathological findings, OCT shows cellular infiltrates in the vitreous, retinal vasculitis and edema, and retinal folds; d–f, resolution phase of EAU (21–28 days post immunization), partial clearing of ocular media facilitate OCT visualization of cellular infiltration in the vitreous (d), retinal folds (e, arrow), choroiditis (e, yellow arrow) as well as degenerating PRL (f). Eighteen mice were included for histological examination, and eyes of 2–3 mice were harvested at individual time point.