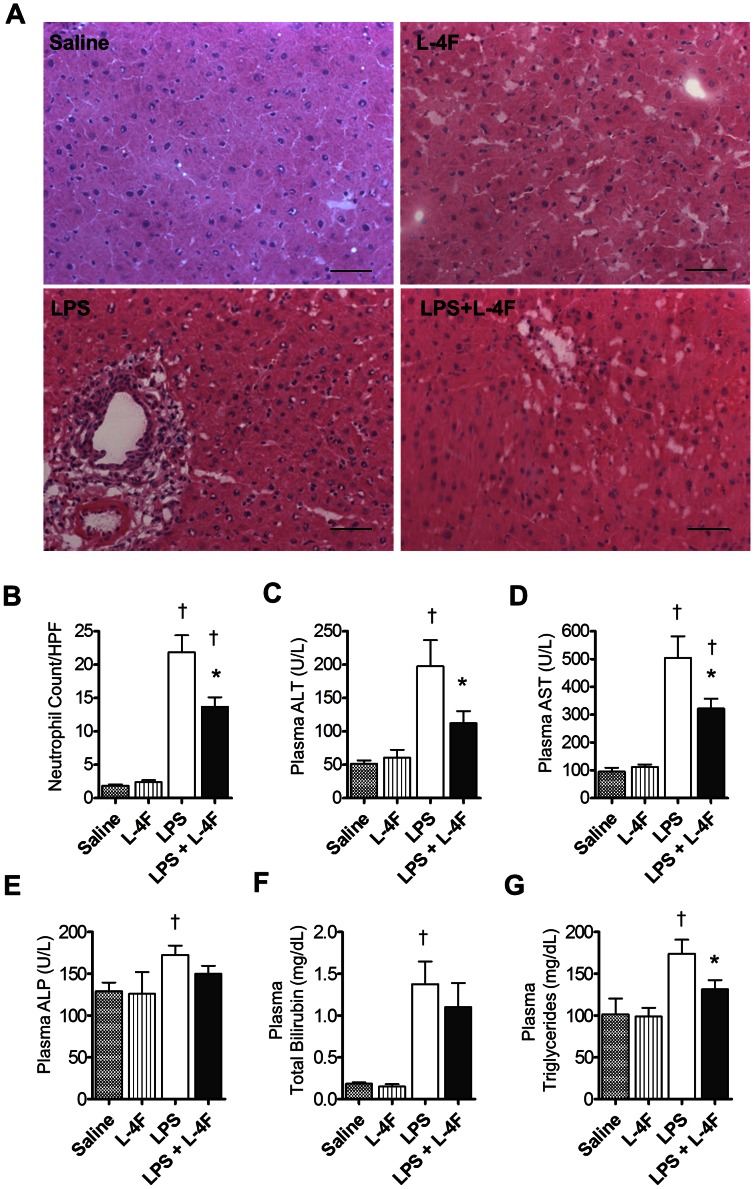
Figure 3. L-4F inhibits liver inflammation in endotoxemic rats.
A: Liver sections (×20), stained with H&E. Liver sections from saline and L-4F-treated animals showed normal morphological and histological features without signs of inflammation or tissue damage. Liver sections from rats treated with LPS demonstrated significant infiltration of inflammatory cells, whereas liver sections from rats treated with LPS and L-4F had reduced infiltration of inflammatory cells. Scale bars, 50 µm. B: Blinded analysis of neutrophil infiltration in liver tissue. Neutrophil counts were performed based on the segmented morphology in high power fields (×40) in 30 measurements from 10 different randomly selected portal areas (n = 4/group). C, D, E, F, G: Plasma ALT, AST, ALP, Total Bilirubin, triglycerides, respectively (n = 8–12/group). *P<0.05 vs. LPS, †P<0.05 vs. Saline and L-4F.