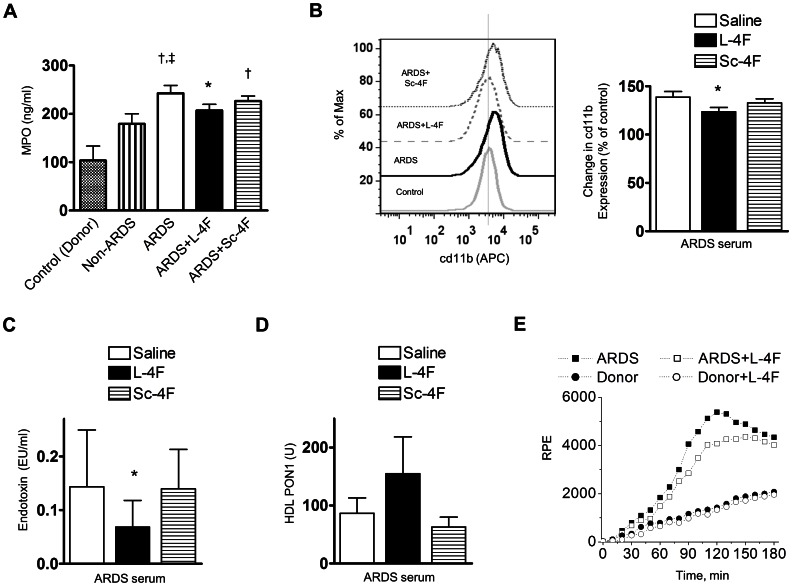
Figure 8. L-4F inhibits inflammatory potential of ARDS serum on human cells.
In A, B, C, D: human neutrophils isolated from healthy individuals (Control) were incubated in ARDS or non ARDS patient serum for 1h in the presence of 40 µg/ml L-4F or Sc-4F (n = 5). A: Change in MPO levels in cell media (ARDS and non-ARDS serum). B: Measurements of cd11b expression in neutrophils stained with anti-human cd11b (activation epitope) allophycocyanin (APC). A representative histogram of surface expression of cd11b for different treatments (left); statistical data presented as percent changes in cd11b expression (based on mean fluorescent intensity) relative to the saline control (right). Vertical dashed line represents median cd11b activation in control. C: Change in endotoxin levels in ARDS serum. D: Change in HDL-associated PON1 activity in ARDS serum. E: L-4F (40 μg/ml) inhibits superoxide formation by leukocytes mediated by ARDS serum. Superoxide formation was measured with lucigenin-amplified chemiluminescence in freshly isolated human leukocytes at room temperature. A representative example of six consistent experiments is shown. RPE = Relative Photon Emission. *P<0.05 vs. saline-treated LPS or ARDS, †P<0.05 vs. control groups, ‡P<0.05 vs. non-ARDS.