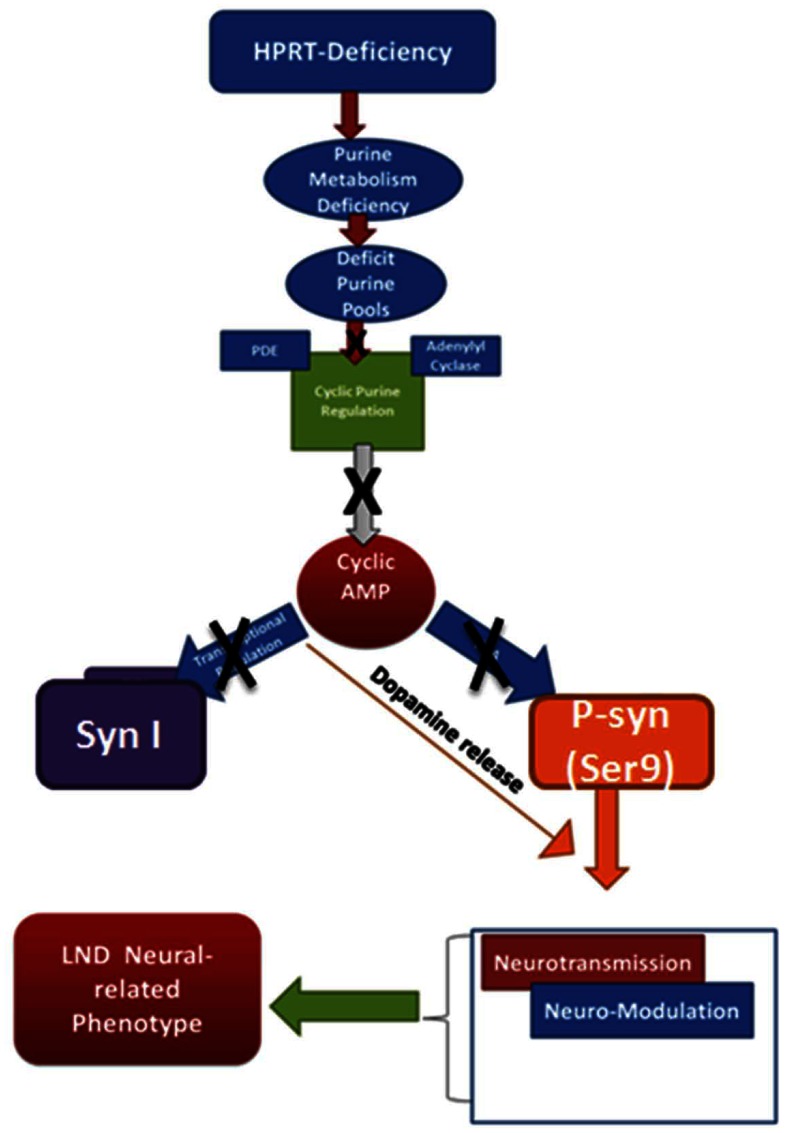
Figure 7. Schematic of the possible mechanisms by which HPRT-deficiency via blunting of cAMP/PKA signaling leads to the neural-related LND phenotype.
HPRT-deficiency is primarily a purine metabolism deficiency that affects the cellular purine pools. The deficit in purine pools causes changes in expression and activity of PDE and/or AC reduces cAMP production. We propose that the cAMP deficit in HPRT-deficient causes a reduction in CREB and thereby expression of neural genes such as Synapsin I. The decrease in PKA activity blunts phosphorylation of substrates, such as p-Syn I (Ser9), which is known to affect neurotransmitter release. We conclude HPRT-deficiency via inhibiting cAMP/PKA signaling could affect neurotransmission and neuro-modulation that underlie the neurological phenotype in LND.