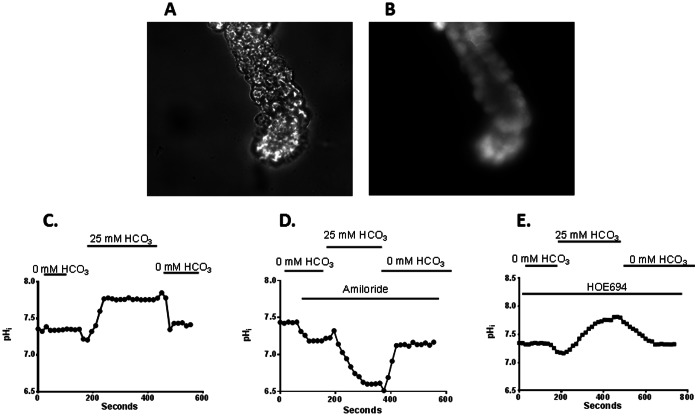
Figure 1. Effect of extracellular HCO3 in the presence and absence of HOE694 on intracellular pH change in crypt glands from proximal colon.
Images of a crypt gland before [A] and after BCECF loading [B]. The BCECF loaded crypts were excited at 490 nm and 440 nm and the emission signal was monitored at 535 nm to derive intracellular pH (pHi). [C] Under basal condition, bath HCO3 increased pHi, while the increased pHi was completely reversed by HCO3 removal. [D] In the presence of amiloride, bath HCO3 reduced the pHi, while the reduced pHi was partially reversed by HCO3 removal. [E] In the presence of HOE694, bath HCO3 increased pHi, while the increased pHi was completely reversed by HCO3 removal. Typical tracing presented is representative of observations in 4 different crypts from 5 different rats.