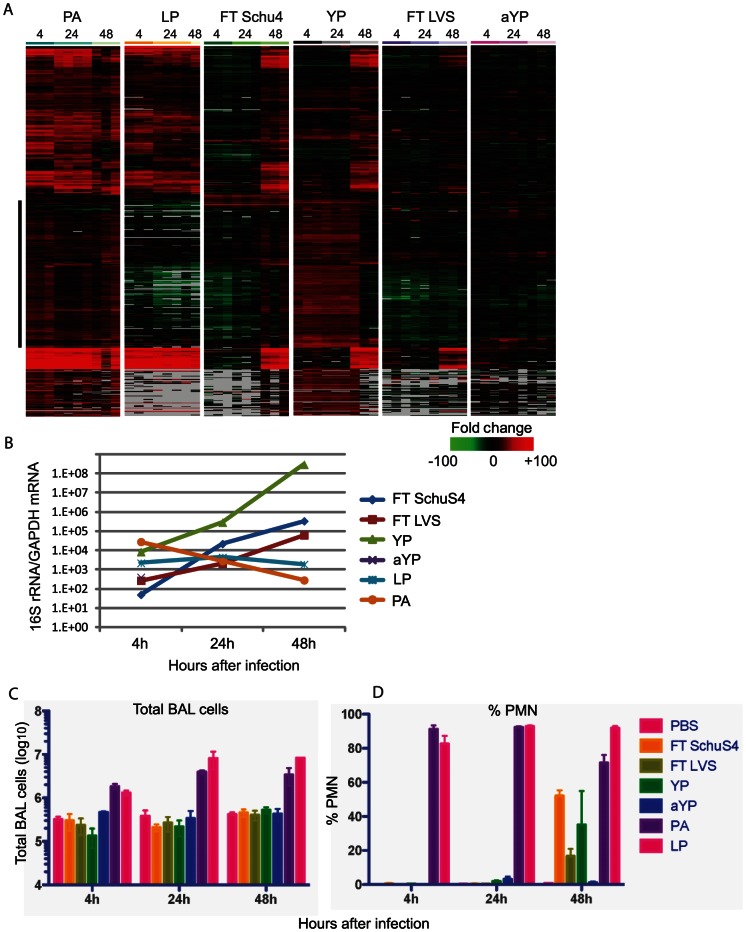
Figure 2. FT SchuS4 induces a limited pulmonary inflammatory response relative to other respiratory pathogens despite active bacterial replication during acute infection.
A. Expression profiles of inflammatory mediators showing differential expression (at least 2-fold in median expression level, p value<0.01, in at least 1 experimental condition) in lung tissue of animals exposed to respiratory pathogens. Each column represents gene expression data from an individual experiment comparing RNA from lung tissue from an infected animal to pooled RNA from lung tissue from mock-infected animals (n = 9). Genes shown in red were up-regulated, genes shown in green were down-regulated and genes in black indicate no change in expression in infected relative to uninfected animals. Grey indicates no data. B. Levels of bacteria present in lung tissue represented by quantitation of 16S rRNA levels. Quantitation of total (C) and PMN (D) cells present in broncoalveolar lavage fluid from animals exposed to PBS, FT SchuS4, FT LVS, YP, aYP, LP and PA, respectively.