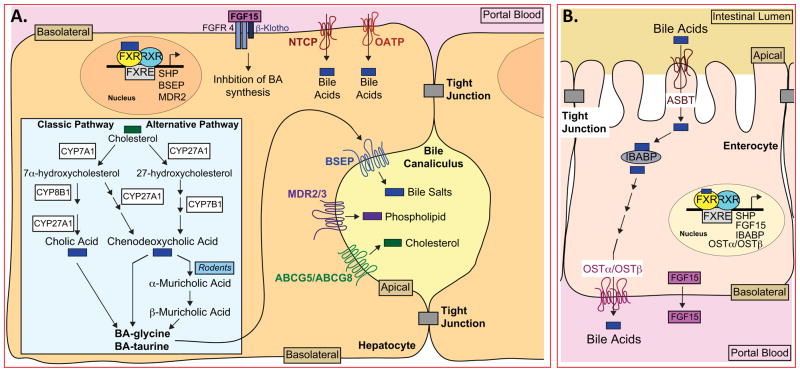
Figure 2. Bile Acid Metabolism in Liver and Intestine.
(A) A cartoon of hepatocytes showing the classic (neutral) and alternative (acidic) bile acid biosynthetic pathways that generate glycine- or taurine- conjugated bile acids (BA), including cholic, chenodeoxycholic and muricholic acids (inset). The location of the lipid transporters BSEP, MDR2/3 and ABCG5/ABCG8 on the apical membrane, and the location of NTCP and OATP transporters that facilitate recovery of bile acids from the blood are also shown. FGF15, secreted into the portal blood from the intestine, is shown bound to FGFR4/β-Klotho, leading to suppression of bile acid (BA) synthesis. Three representative FXR target genes (SHP, BSEP and MDR2) are shown in the nucleus.
(B) A cartoon of enterocytes in the distal ileum showing bile acid absorption from the lumen occurring via ASBT and bile acid efflux out of the cell via OSTα/OSTβ. Representative FXR target genes (SHP, FGF15, IBABP, OSTα and OSTβ) are shown as well as the secretion of FGF15 into the portal blood.