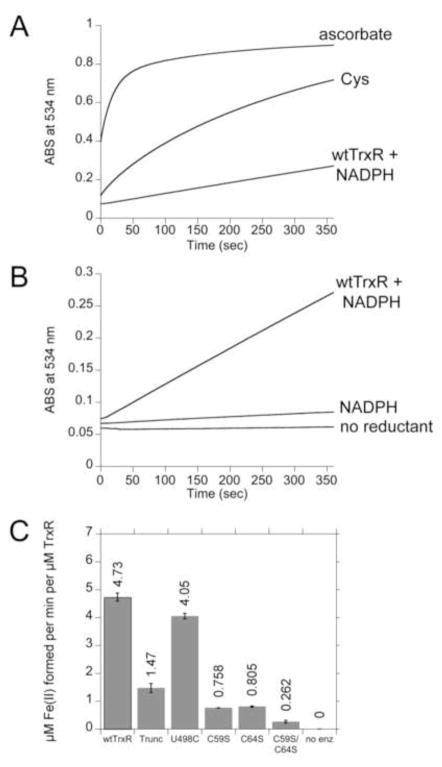
Fig. 7.
Representative experiments showing the rates of Fe(III)-Blm reduction by various reductants. All experiments included 50 μM Fe(III)-Blm and 1 mM BPS. BPS rapidly extracts the Fe(II) from Fe(II)-Blm, forming Fe(II)(BPS)3 which was followed by increased absorbance at 534 nm. (A) The reactions were initiated by the addition of the reductants as indicated (0.2 mM ascorbate, 0.2 mM Cys, or 0.3 μM wtTrxR and 0.4 mM NADPH). (B) An expanded view showing the rate of Fe(III)-Blm reduction catalyzed by wtTrxR compared to NADPH alone or no reductant. (C) Rates of reduction of Fe(III)-Blm by wtTrxR and its site-directed variants. For C, the trace amounts of reduction catalyzed by NADPH alone were subtracted to determine the net rates for each TrxR variant.