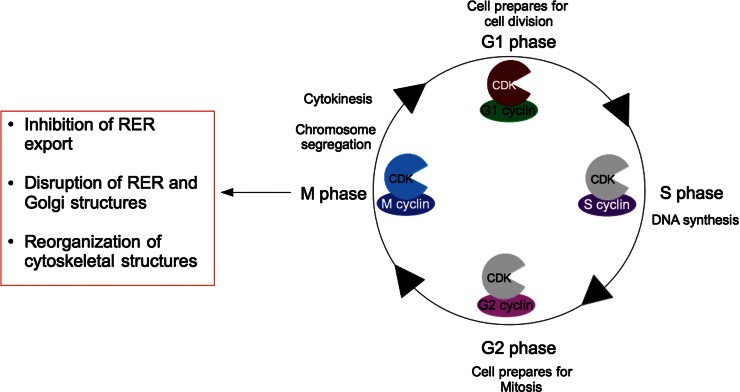
Figure 2.
A representation of a typical eukaryotic cell division cycle. The four major phases of the cell division cycle, G1 (gap) phase, S (synthesis) phase, G2 and M (mitosis) phases, are shown. Different cyclins and CDKs function during specific cell cycle phases to drive phase-specific events. Highlighted in the figure are the key processes of the secretory pathway that are inhibited during M phase (see text for details).