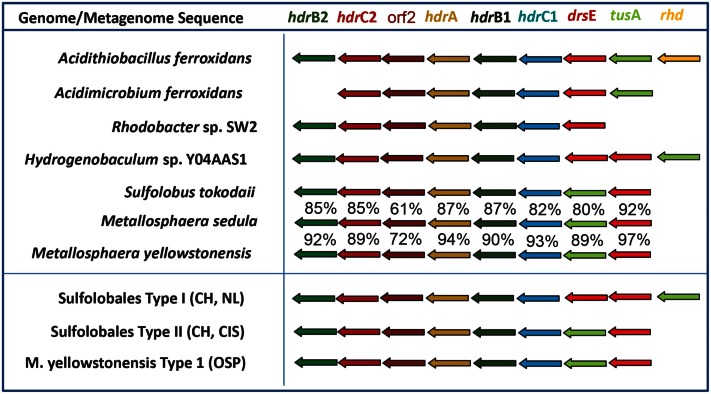
Figure A3.
Conservation of open reading frames found in the heterodisulfide reductase (HDR) gene complex of several acidophilic bacteria and archaea known to be utilized during the oxidation of reduced sulfur. Highly syntenous components of the HDR-gene complex are conserved in several of the thermophilic archaea found in YNP, as well as bacteria within the order Aquificales (Takacs-Vesbach et al., 2013). Percent amino acid similarities of the deduced HDR proteins are shown for M. sedula and M. yellowstonensis relative to S. tokodaii. The Sulfolobales Type I and Hydrogenobaculum sp. Y04AAS1 have two copies of drsE [gene names: hdrB1/hdrB2 = heterodisulfide reductase, subunit B (COG2048); hdrC1/hdrC2 = heterodisulfide reductase, subunit C (COG1150); orf2 = hypothetical conserved protein; hdrA = heterodisulfide reductase, subunit A (COG1148); dsrE = peroxiredoxin family protein (COG2210); tusA = sirA family of regulatory proteins; rhd = rhodanese-related sulfurtransferase (COG0607)].