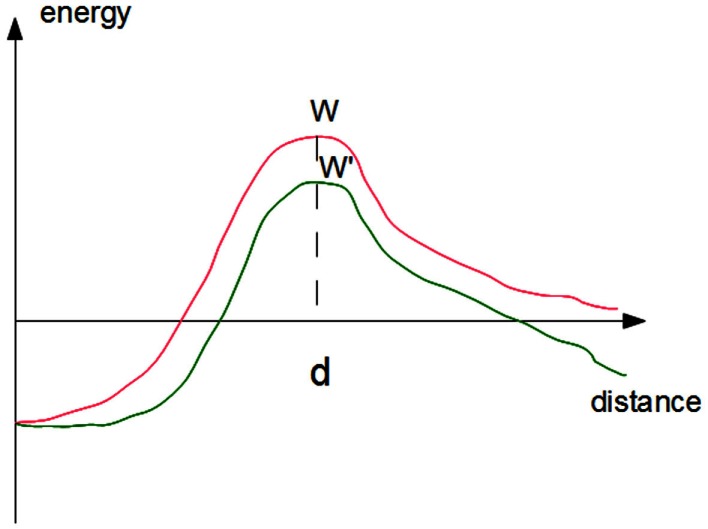
Figure 2.
Effect of forces on the kinetics of bond rupture. The simplest approximation consists of representing the free energy of a ligand-receptor complex as a simple function of the distance between ligand and receptor surfaces (red curve). Rupture requires the crossing of an energy barrier of height W. The rupture rate may be viewed as the product of the frequency of attempts at crossing times the success probability that is proportional to Boltzmann’s factor exp(−W/kBT). Applying a force will decrease the barrier height by the product F.d, i.e., the force times the distance between the barrier and the equilibrium distance, thus multiplying the escape frequency by exp(Fd/kBT).