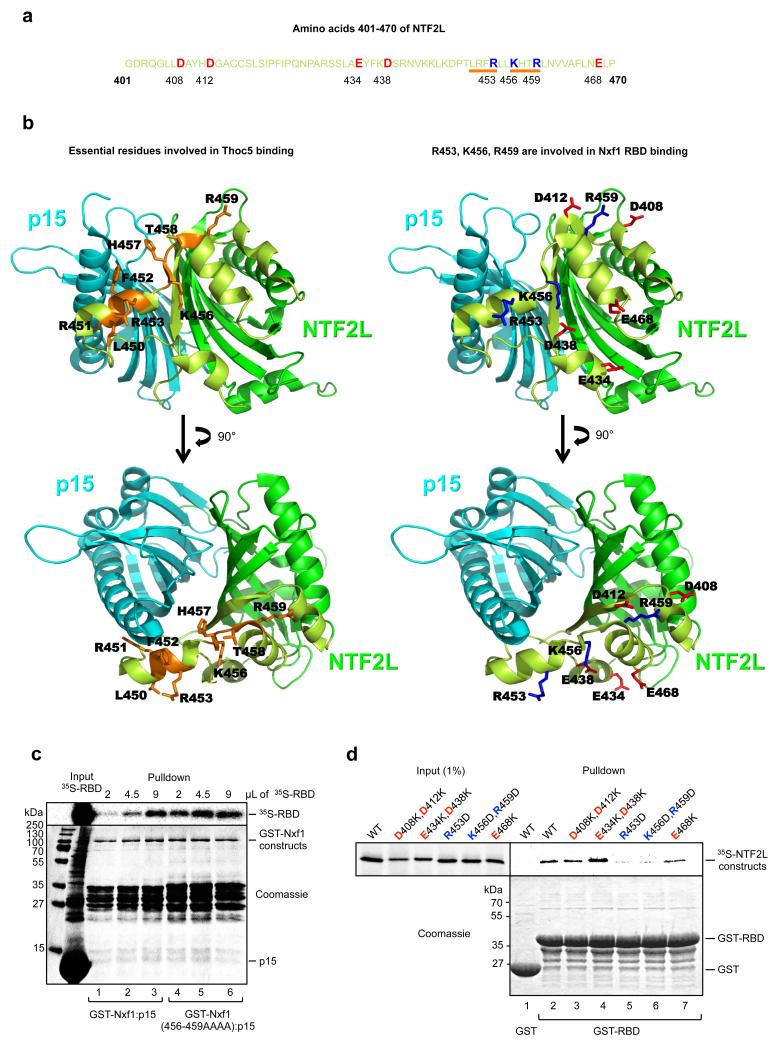
Figure 3. Identification of the NTF2L:RBD binding interface.
(a) Sequence of the region of the NTF2L domain targeted by the mutagenesis. Targeted residues are highlighted as red for acidic and blue for basic. Orange bars indicate the most crucial residues involved in Thoc5 binding (Katahira J. et al, EMBO J., 2009 Mar 4;28(5):556-67) that also enhance Nxf1 interdomain interaction when mutated to alanines (in case of 456-459). (b) Positions of the above mentioned residues on NTF2L:p15 structure (1JKG) using the same colors as in (a). p15 is in cyan, the NTF2L domain is in dark green, targeted region within the NTF2L domain is in light green. (c) Nxf1(456-459AAAA) mutant binds Nxf1 RBD more efficiently than wild type Nxf1. GST pulldowns with the indicated fusions and increasing amounts of 35S-RBD. (d) GST pulldown experiment using GST-RBD and the indicated in vitro translated mutants of the NTF2L domain of Nxf1.