Figure 1.
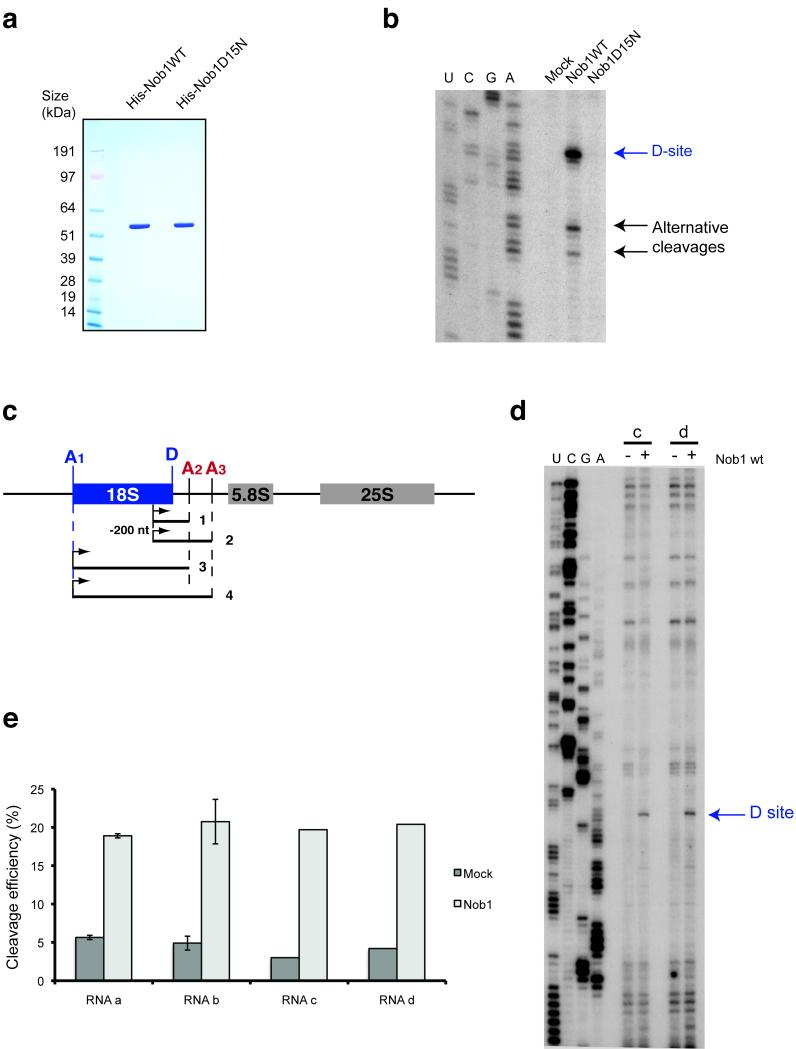
In vitro RNA cleavage by Nob1 is not affected by sequences 3′ to site A2. (a) Recombinant forms of wild-type and mutant Nob1 were purified over nickel resin followed by gel filtration. 2 μg of each protein was loaded on an SDS-gel and Coomassie stained. (b) Cleavage assay on in vitro transcribed RNA. In vitro transcribed RNA was incubated with wild-type or mutant Nob1 and analyzed by primer extension. The major cleavage at site D is indicated, as are alternative cleavage sites, which were previously observed in vitro at sequences similar to site D 11. (c) Structures of long RNA substrates, mimicking the pre-rRNA before A2 cleavage (substrates 2 and 4) and after A2 cleavage (substrates 1 and 3). (d,e) The cleavage efficiency was determined by primer extension on the two longer RNA substrates (3 and 4) (d) and quantified using northern hybridization data (e). The ratio between cleaved fragment (D-A2) and intact RNA is presented as a histogram. These experiments were repeated for the shorter RNAs (substrates 1 and 2) but were performed only once for substrates 3 and 4 (with 5′ ends at site A1) due to the difficulties in purifying these long RNA species.