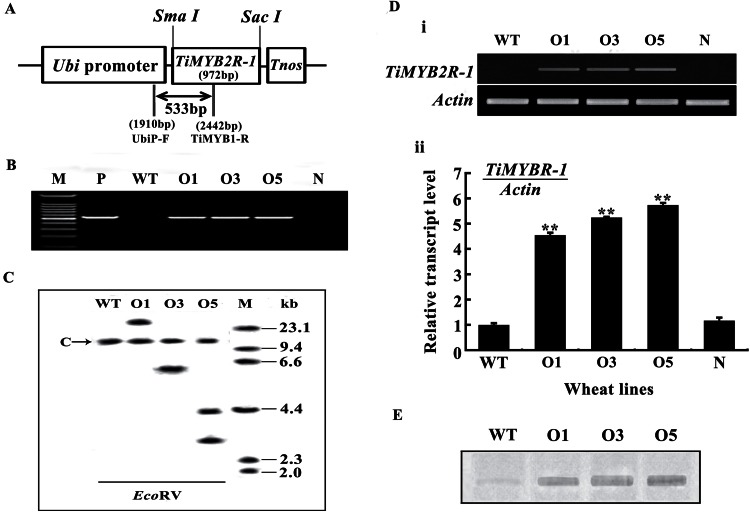
Fig. 4.
TiMYB2R-1 transformation vector and molecular characterization of transgenic wheat. (A) In transformation vector pA25-TiMYB2R-1, the TiMYB2R-1 gene was driven by the maize ubiquitin (Ubi) promoter and terminated by Tnos. The arrow indicates the region amplified in the PCR assays using UbiP-F and TiMYB1-R primers and used for the Southern blot probe. (B) PCR pattern of TiMYB2R-1 transgenic and wild-type wheat plants using the transgene-specific primers UbiP-F and TiMYB1-R. M, 100bp DNA ladder; P, transformed vector plasmid pA25-TiMYB2R-1. (C) A Southern blot analysis of EcoRV-digested genomic DNAs from non-transformed and TiMYB2R-1 transgenic plants hybridized with an amplified fragment specific for the transgene. M, λDNA/HindIII markers. C band indicates the common bands in all wheat plants. (D) RT–PCR (i) and Q-RT–PCR (ii) analyses of TiMYB2R-1 transcript levels in the roots of T5 transgenics and control plants. In Q-RT–PCR analysis, three replicates for each sample were averaged, with the standard error of the mean (SE) indicated. Asterisks indicate statistically significant variation (**P < 0.01). (E) Western blot pattern of TiMYB2R-1 protein expression in roots of Ggt-resistant T5 transgenics and susceptible wild-type wheat lines. WT, non-transformed wheat Yangmai 12; O1, O3, and O5, three TiMYB2R-1 transgenic lines; N, segregant plants lacking TiMYB2R-1.