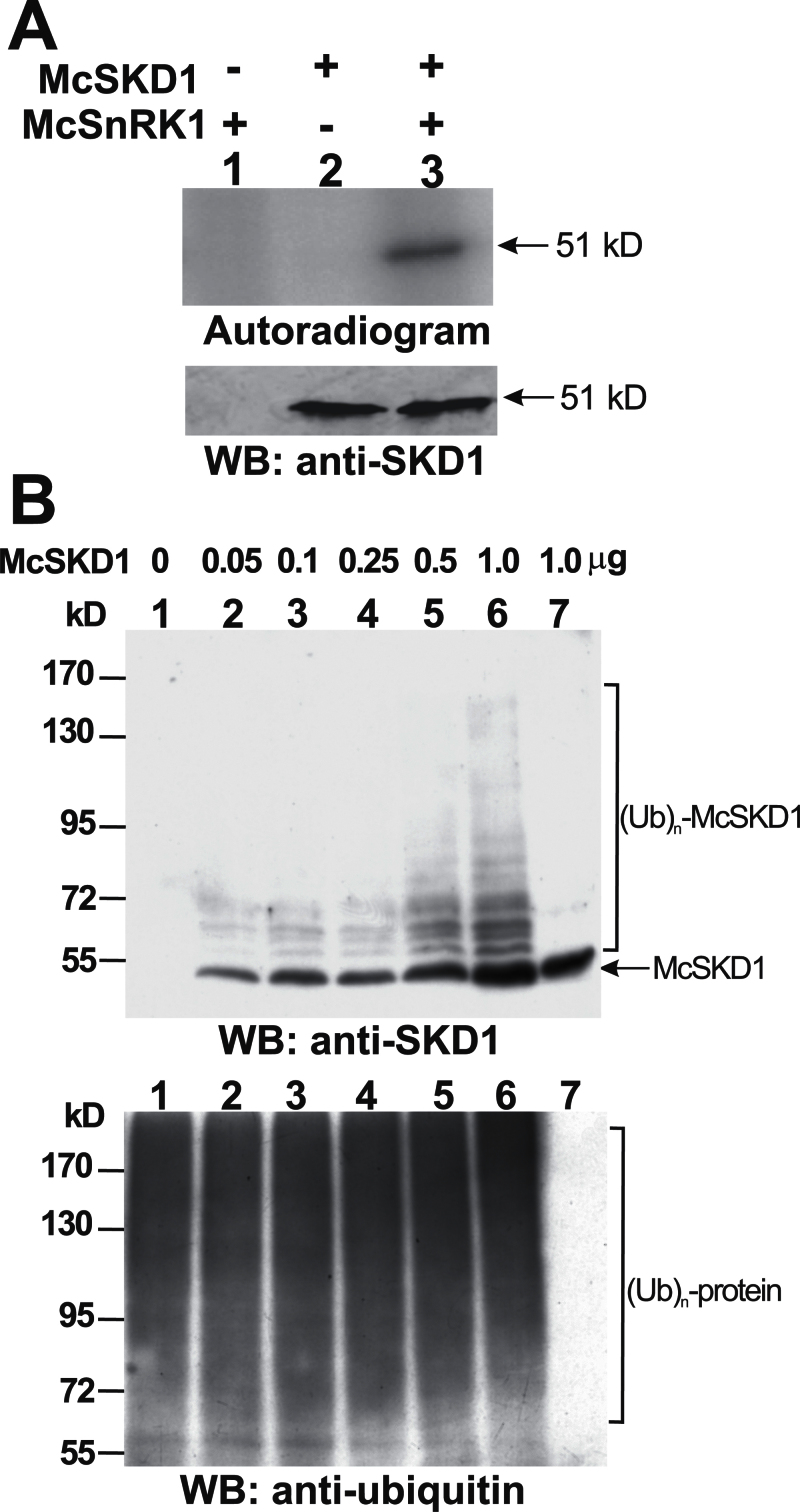
Fig. 5.
In vitro analysis of McSKD1 phosphorylation by McSnRK1 and ubiquitination by McCPN1. (A) The substrate phosphorylation reaction by McSnRK1 was performed using McSKD1 as the substrate in the presence of 10mM N-ethylmaleimide (NEM) (lanes 1–3). A 1 μg aliquot of purified McSKD1-(His)6 was added alone (negative control) or with 1 μg of purified GST–McSnRK1 to the in vitro kinase reaction. After separation by 10% SDS–PAGE, the resulting gels were transferred to a PVDF membrane and autoradiographed using a PhosphorImager. Subsequently, the same membrane was analysed by western blotting using anti-McSKD1 antiserum. The arrow indicates the position of McSKD1. (B) In vitro ubiquitination reaction by McCPN1 was performed using McSKD1 as the substrate. Various concentrations of purified McSKD1-(His)6, up to 1 μg, were added to the complete in vitro ubiquitination mixture containing McCPN1 as E3 (lanes 1–6). Lane 7 is a reaction without E3 as a negative control showing that no ubiquitination occurred. Western blotting using anti-SKD1 antiserum was used to detect McSKD1 and its ubiquitin-conjugated forms (top), and anti-ubiquitin antibody was used to detect protein–ubiquitin conjugates (bottom). The arrow indicates the position of McSKD1 (51kDa) and the laddered bands indicate ubiquitin–McSKD1 conjugates.