Figure 2.
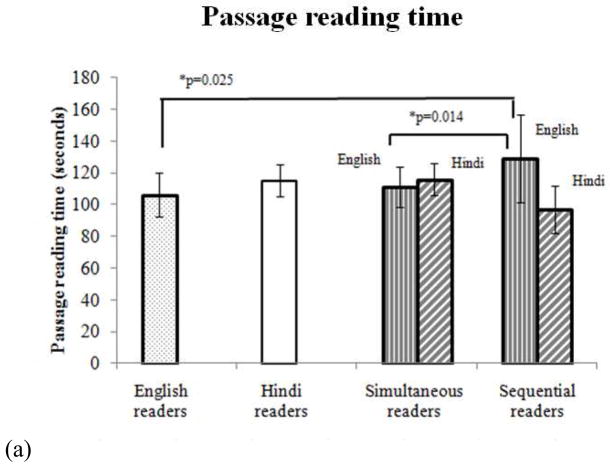
Figure 2(a). Passage reading time for English and Hindi. The plot shows average passage reading times for English (average±stdev; 106.06±13.84) and Hindi (115.16±10.21) monolingual readers, early simultaneous bilingual readers reading in English (111.08±12.79) and Hindi (115.90±10.21) and late sequential bilingual readers reading in English (129.06±27.8) and Hindi (96.96±15.05). A significant difference is observed between simultaneous and sequential readers in the time taken to read English passage (Mann Whitney test, p=0.014). The sequential readers also differed when compared to English monolingual readers in time taken to read the passage (two sample t-test, t13=2.536, p=0.025).
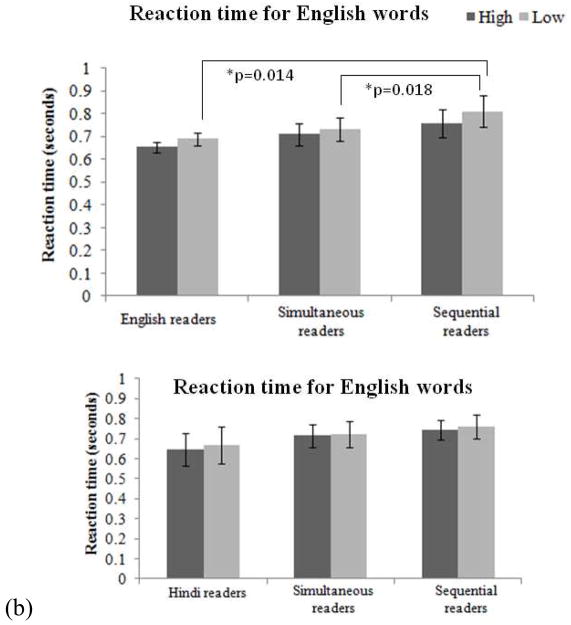
Figure 2(b). Reaction time for reading English and Hindi words. Top panel shows reaction time to read English high and low frequency words in English readers (high: 0.65±0.02 sec; low: 0.68±0.03 sec), simultaneous (high: 0.71±0.04 sec; low: 0.73±0.05 sec) and sequential readers (high: 0.75±0.06 sec; low: 0.81±0.07 sec). Sequential readers differ from monolingual English readers while reading low frequency words (t-test, t9=− 3.040, p<0.014) and simultaneous readers (t-test, t9=−2.87, p<0.018). The bottom panel shows reaction times for reading high and low frequency Hindi words by monolingual Hindi readers (high: 0.64±0.08 sec; low: 0.66±0.09 sec), simultaneous (high: 0.71±0.05 sec; low: 0.72±0.06 sec) and sequential readers (high: 0.74±0.04 sec; low: 0.76±0.05 sec). No between group differences for reading either high or low frequency Hindi words are observed. The error bars depict the standard error of mean.