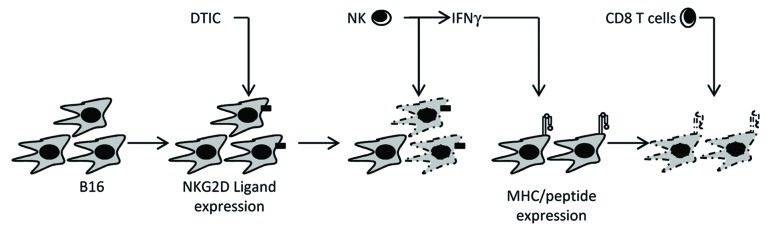
Figure 1. Dacarbazine-mediated immune antitumor effects. Based on results obtained in a subcutaneous B16F10 mouse model, we concluded that: (1) after dacarbazine (DTIC) administration, tumor cells express NKG2D ligands; (2) these ligands promote the activation of natural killer (NK) cells, resulting in cytotoxic functions and interferon γ (IFNγ) secretion; (3) IFNγ stimulates the expression of MHC class I/peptide complexes on the surface of DTIC-resistant tumor cells, whereupon tumor-specific CD8+ T cells can proceed to antigen-dependent lysis.
