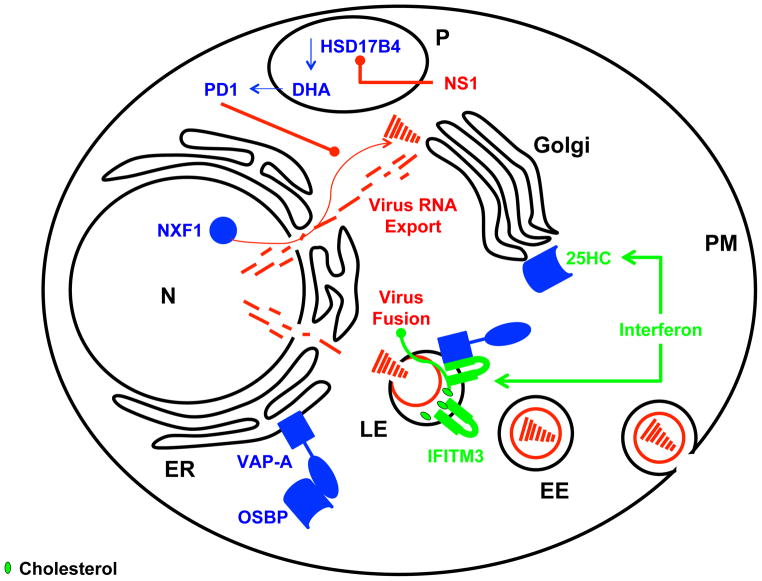
Figure 1.
The interferon response upregulates expression of IFITM proteins and increases the conversion of cholesterol to 25HC
IFITM3 expressed at late endosomal compartments (LE) interacts with vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP)-associated protein A (VAPA) disrupting the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) resident complex between oxysterol binding protein (OSBP) and VAPA. 25-hydroxycholesterol (25HC) mediates the translocation of OSBP to the Golgi and together, these intracellular changes lead to cholesterol accumulation in LE, blocking virus entry. The docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) derived lipid mediator protectin D1 (PD1) inhibits nuclear export of viral RNAs mediated by NXF1. Biosynthesis of DHA is crucially dependent on peroxisomal β-oxidation catalyzed by hydroxysteroid (17-beta) dehydrogenase 4 (HSD17B4). Influenza virus NS1 antagonizes metabolism of DHA derived lipid mediators by its inhibitory interaction with HSD17B4. Host factors, viral factors and interferon stimulated factors are colored in blue, red and green respectively; arrows indicate activation/stimulation or inhibition (rounded ends); plasma membrane (PM), early endosome (EE), late endosome (LE), endoplasmic reticulum (ER), nucleus (N) and peroxisome (P).