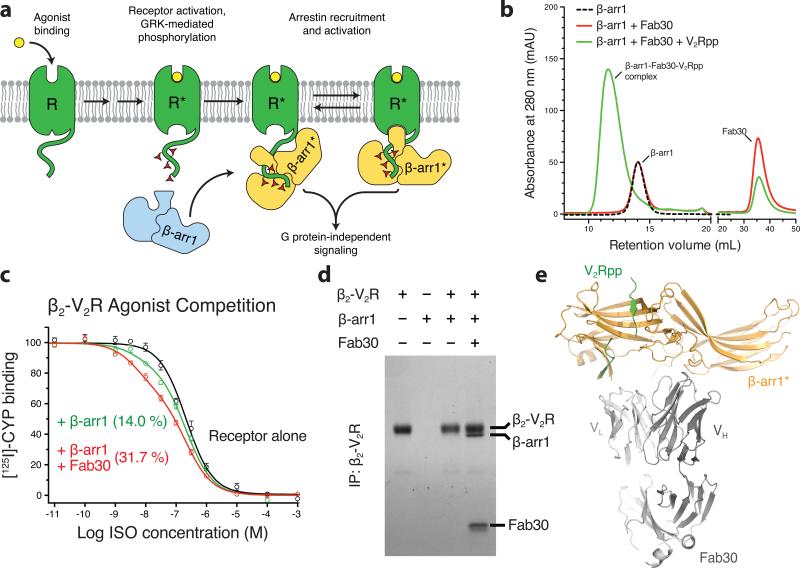
Figure 1. Fab30 specifically recognizes and stabilizes an active state of β-arrestin1.
a, G protein coupled receptors are phosphorylated following activation, leading to the binding of arrestins. Interactions between the phosphorylated receptor and β-arrestin1 lead to β-arrestin1 activation and the subsequent blockade of G protein signaling and initiation of β-arrestin1 signaling pathways. b, Interaction between β-arrestin1 and Fab30 requires the presence of V2Rpp in a size exclusion assay. c, The formation of a complex between a GPCR and β-arrestin allosterically leads to an enhanced affinity of agonist for the receptor, termed the “high agonist affinity state.” Therefore, the fraction of receptor in the high agonist affinity state reflects the extent of complex formation between receptor and β-arrestin. In a radioligand competition binding assay using 125I-cyanopindolol as the probe and the agonist isoproterenol (Iso) as the competitor, β-arrestin1 alone shifts a small portion (14%) of receptors into the high agonist affinity state. Fab30 significantly amplifies this effect (31%) (n=3, p<0.0001 in F test). d, In a pull-down assay, phosphorylated β2-V2R chimera shows appreciable binding to β-arrestin1 only in the presence of Fab30. e, Overall structure of the β-arrestin1:V2Rpp:Fab30 complex.