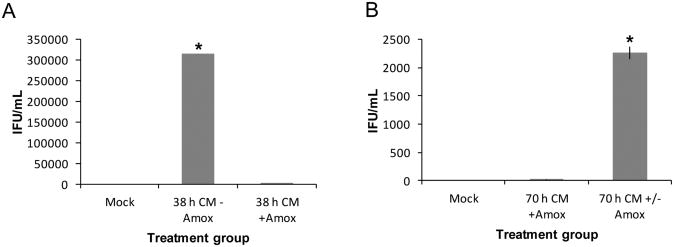
Figure 1.
Amox exposure reversibly reduces C. muridarum infectivity in culture. BM1.11 monolayers were either mock- or C. muridarum (CMW)-infected. At 8 hpi, cultures were refed with medium (+/-) amox; 30 h later, some replicates were harvested for TEM (Fig. 2) or titer analyses (panel A). Other amox-exposed replicates were refed with either antibiotic-free medium (70 h CM +/- Amox) or medium (+) amox (70 h CM + Amox) at 38 hpi and allowed to incubate until 70 hpi (panel B). Triplicate inclusion counts were averaged and used to calculate inclusion forming units (IFU)/mL. The average of three biologic replicates ± SEM from one representative experiment is shown. Groups significantly different from the diluent-exposed, infected control are indicated by asterisks (*), P ≤ 0.05 was considered significant. These results are representative of three independent experiments.