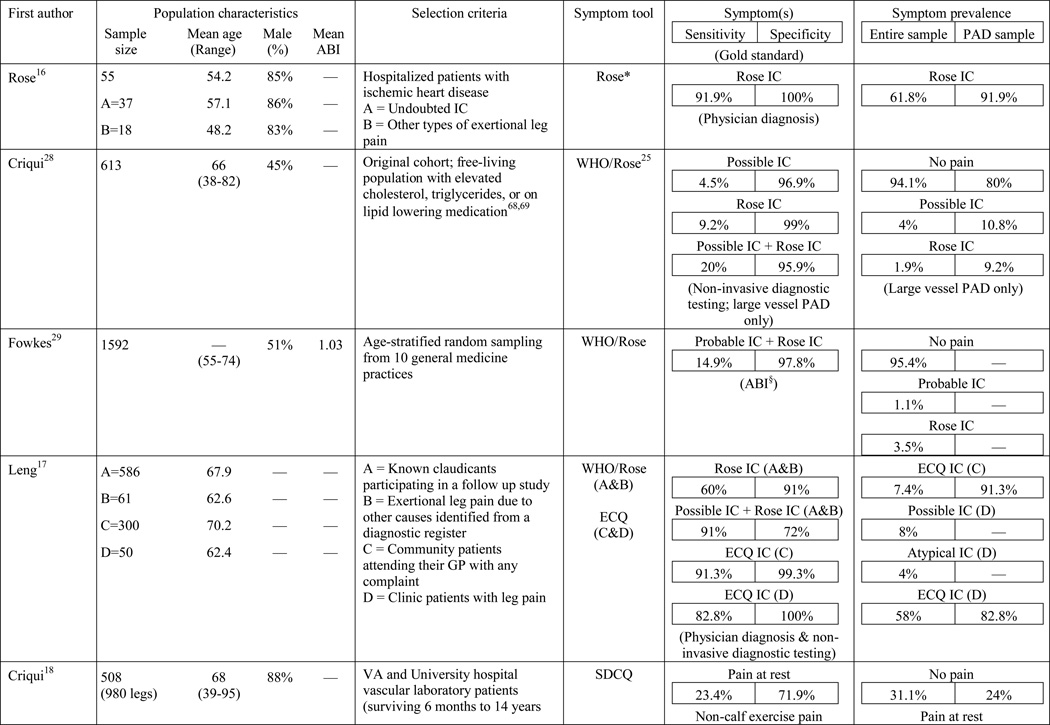
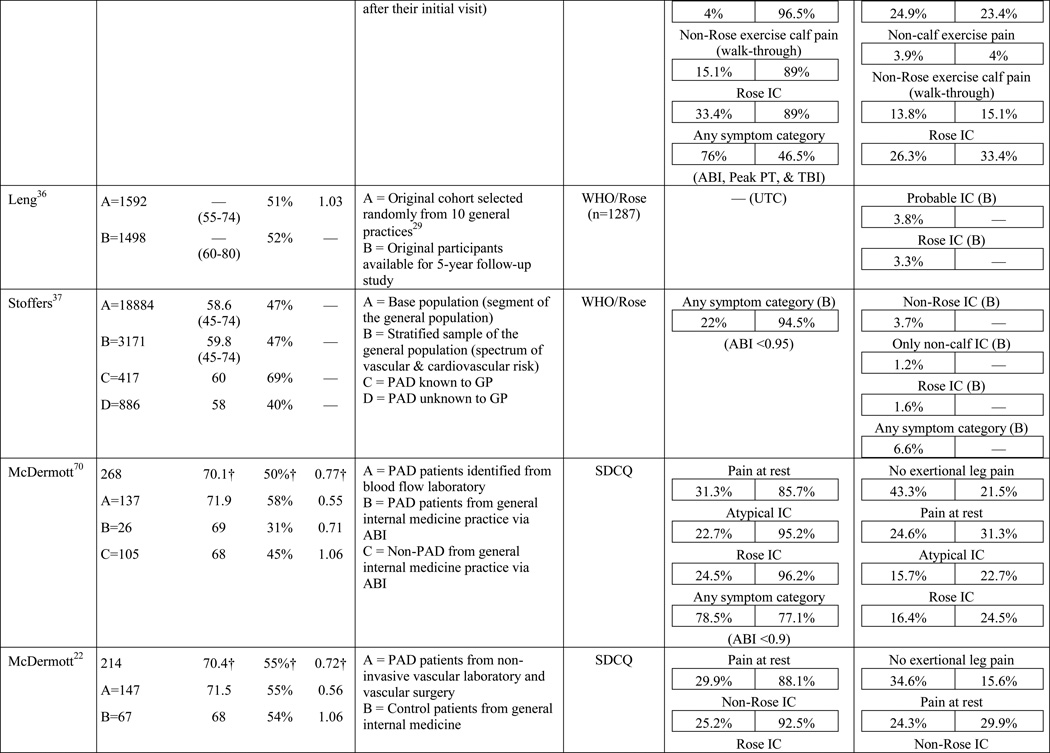
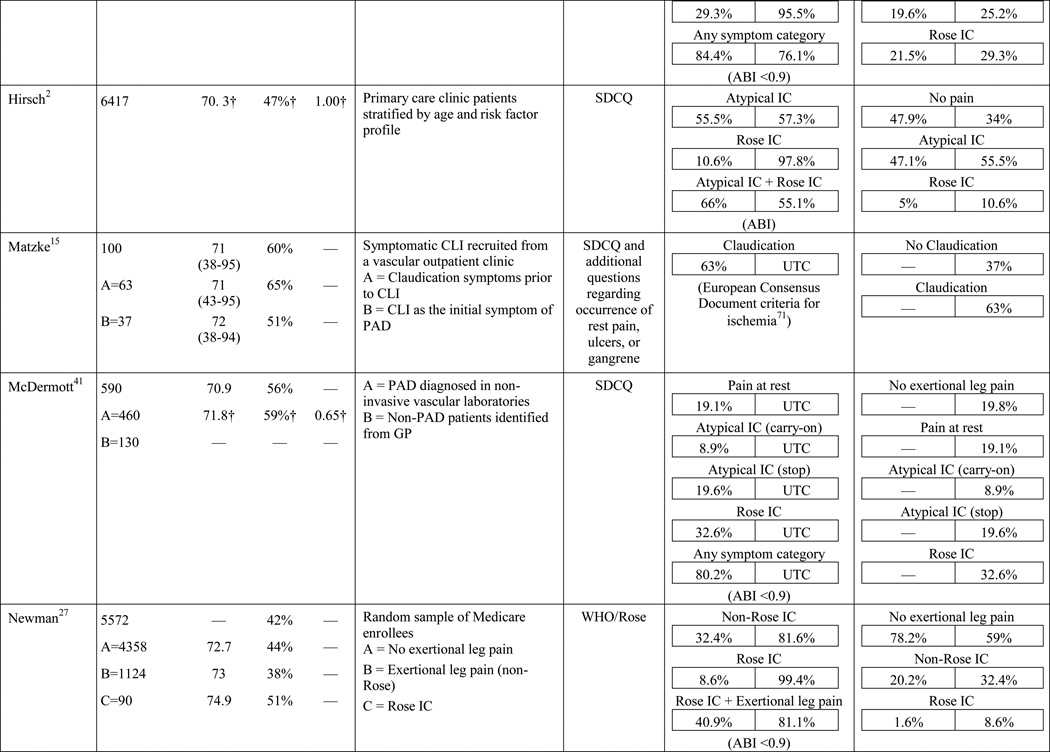
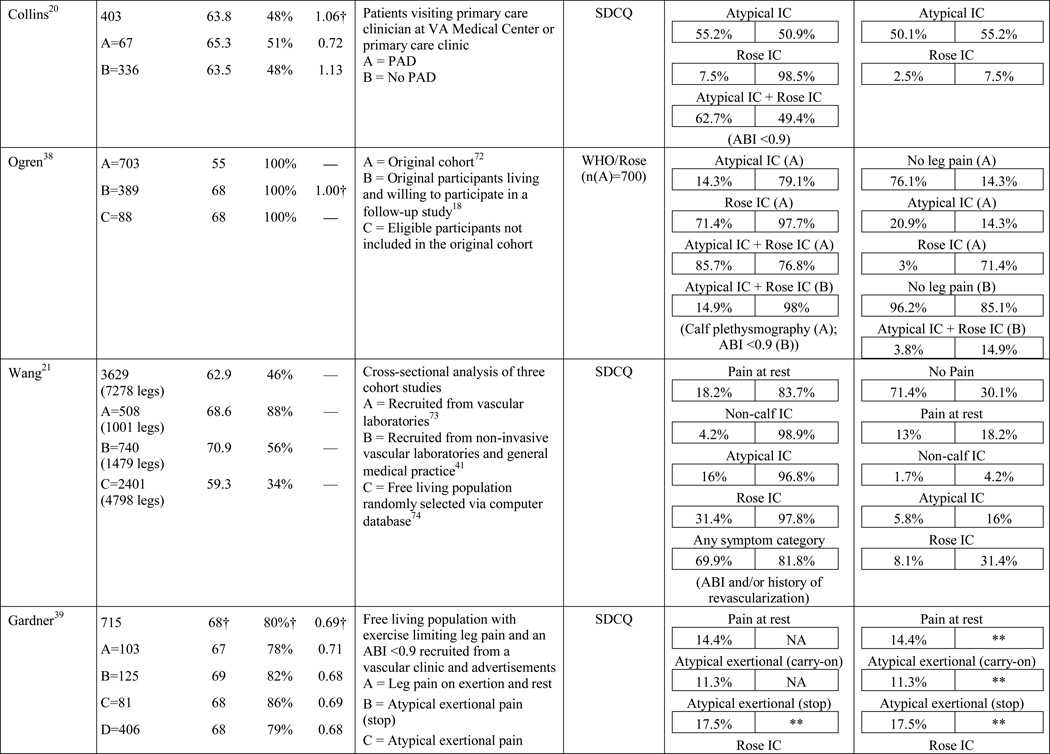
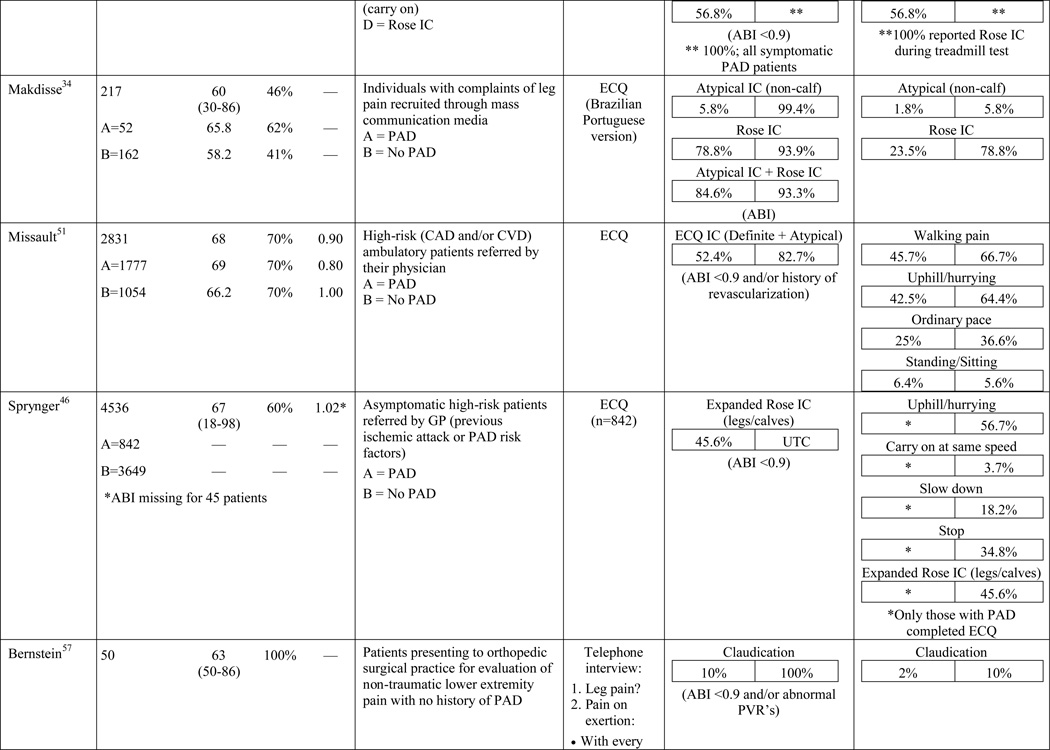
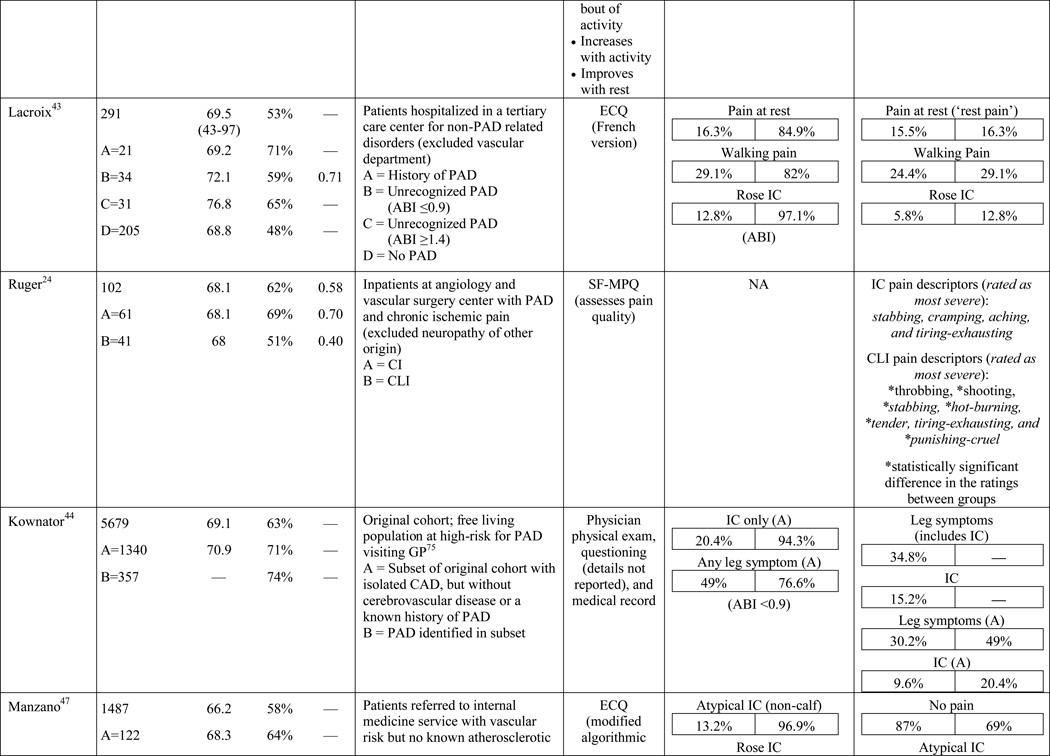
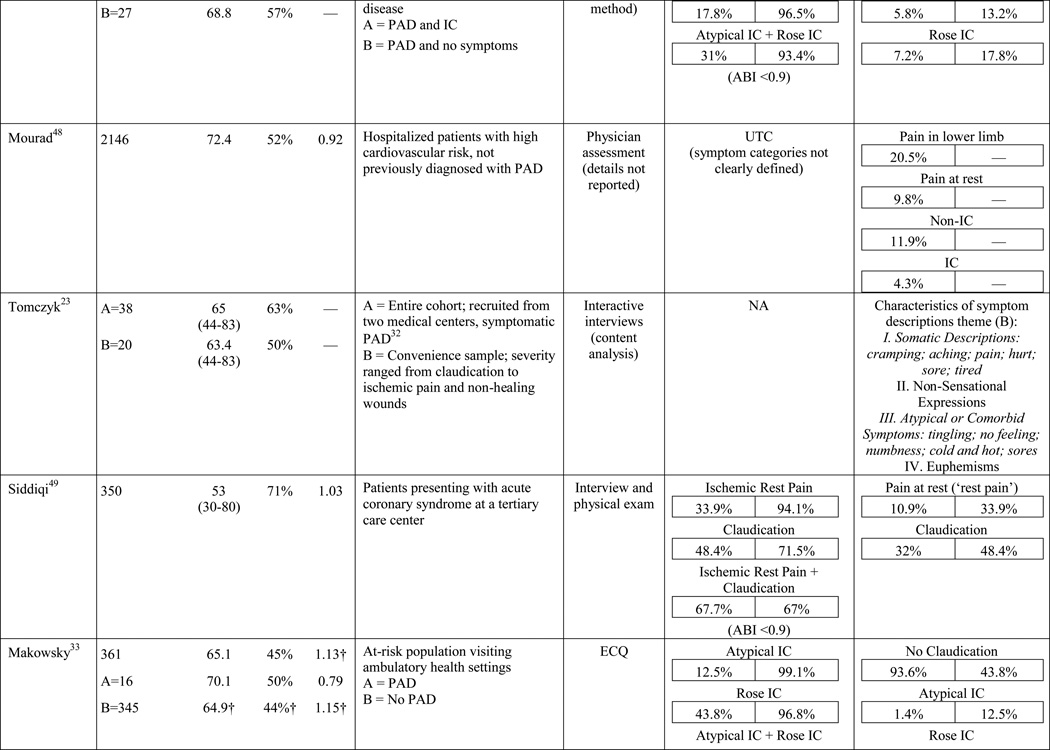
Table 1.
Results of the structured review.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
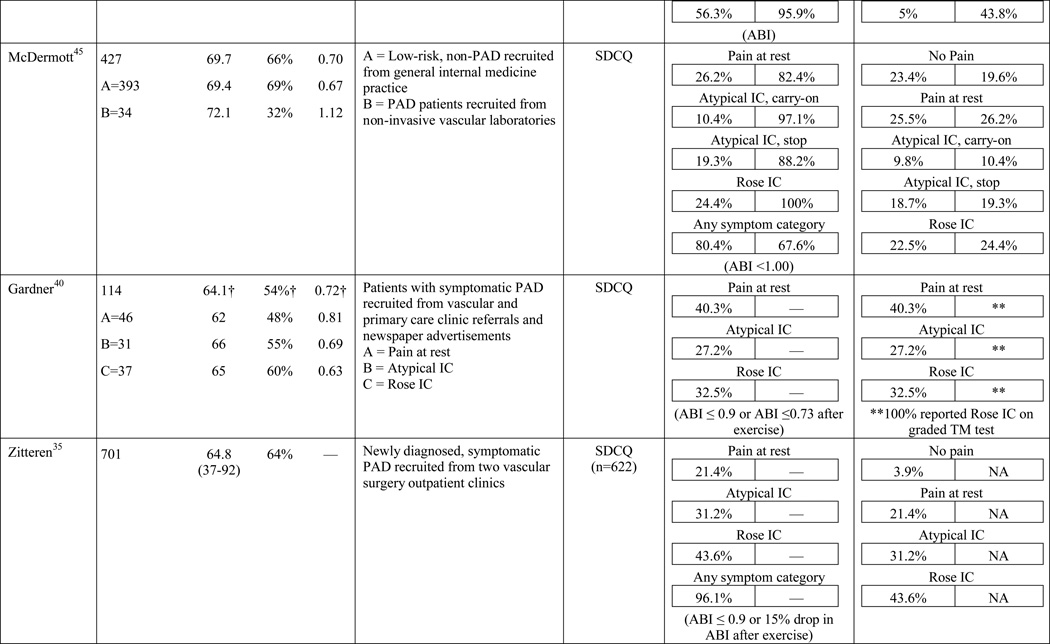 |
ABI=ankle-brachial index; PAD=peripheral artery disease; — =not reported; IC=intermittent claudication; *Rose questionnaire adopted by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 1968 for use in epidemiological surveys; §PAD diagnostic criteria was ABI ≤ 0.9 unless indicated otherwise76; GP=General Practitioner; ECQ=Edinburgh Claudication Questionnaire; VA=Veterans Affairs; SDCQ=San Diego Claudication Questionnaire; Peak PT=peak velocity in the posterior tibial artery; TBI=toe-brachial index; UTC=unable to calculate; †=calculated; CLI=critical limb ischemia; CAD=coronary artery disease; CVD=cerebrovascular disease; PVR=pulse volume recordings; CI=chronic ischemia; SF-MPQ=Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire; NA=not applicable
