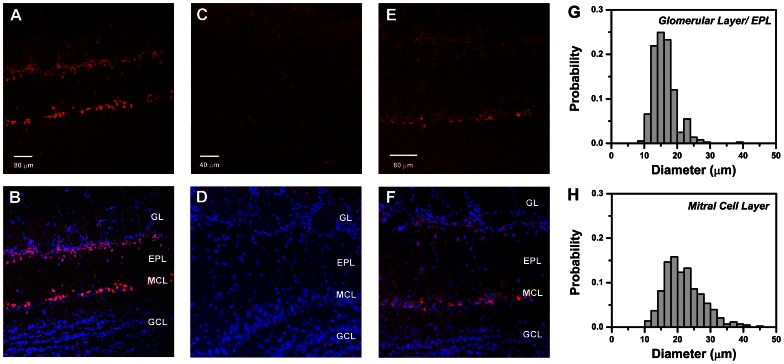
Figure 8. Cellular localization of CCKB receptor immunoreactivity in mouse olfactory bulb.
A. Confocal fluorescent image of anti-CCKB receptor antibody binding to a horizontal section of an olfactory bulb from a CD-1 mouse, visualized with Alexa Fluor 633-conjugated secondary antibody (red). Strong immunoreactivity appears in a superficial zone including the inner margins of the glomerular layer (GL) and the distal part of the external plexiform layer (EPL), and in a deeper zone corresponding to the mitral cell body layer (MCL). Scale bar: 80 µm. B. Composite image showing overlay of CCKB immunoreactivity in A (red) with fluorescent DAPI-stained nuclei (blue) to highlight the positions of cell bodies. Similar cellular distributions of immunoreactivity were obtained in 29 sections from 5 mice. C. Confocal fluorescent image (Alexa Fluor 633) of horizontal section of olfactory bulb from a 129-Cckbrtm1Kpn/J (CCKB knockout) mouse, processed with the same antibody and protocol as in A. Scale bar: 40 µm. D. Composite image from the CCKB knockout obtained by overlaying Alexa Fluor 633 fluorescence in C (red) with DAPI stained nuclei (blue). A similar absence of cell labeling was seen in 4 other sections of the bulb from the same mouse. E. Confocal fluorescent image of anti-CCKB receptor binding to horizontal section from a CD-1 mouse, using B2 antibody of Mercer & Beart (2000) [42](1∶100 dilution). Scale bar: 80 µm. F. Composite image combining E (red) with fluorescent DAPI stained nuclei (blue). G. Distribution of cell body diameters in the GL and EPL that were immuno-positive for CCKB receptor. H. Distribution of cell body diameters in the glomerular layer and EPL that were immuno-positive for CCKB receptor. Histograms in G–H are normalized to total cell count. Note: Small non-nucleated fluorescent filaments visible in some sections are due to non-specific background staining of erythrocytes and appear in controls not treated with primary antibody. Abbreviations: GL, glomerular layer; EPL, external plexiform layer; MCL, mitral cell layer; GCL, granule cell layer.