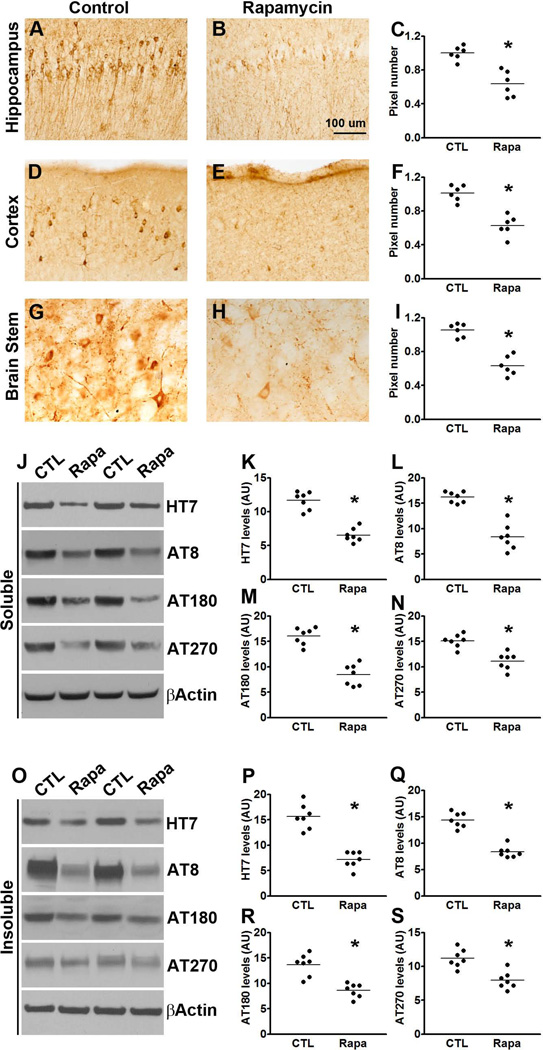
Figure 4. Rapamycin decreases tau pathology in P301S mice.
(A-I) Microphotographs and quantitative analyses of P301S mice treated with rapamycin or control diet and stained with the AT8 antibody. (J) Western blots of soluble tau extracted from the brains of P301S mice treated with rapamycin or control diet and probed with the indicated antibodies. (F-H) Quantitative analyses of the blots show that rapamycin treatment significantly decreased the levels of tau phosphorylated at the AT8, AT180 and AT270 epitopes. (O) Western blots of insoluble tau extracted from the brains of P301S mice treated with rapamycin or control diet and probed with the indicated antibodies. (P-S) Quantitative analyses of the blots show that rapamycin significantly decreased the levels of tau phosphorylated at the AT8, AT180 and AT270 epitopes. Quantifications of the Western blots were done by normalizing the protein of interest to β-actin, which was used as a loading control. Data are presented as means ± SEM and analyzed by student’s t-test.