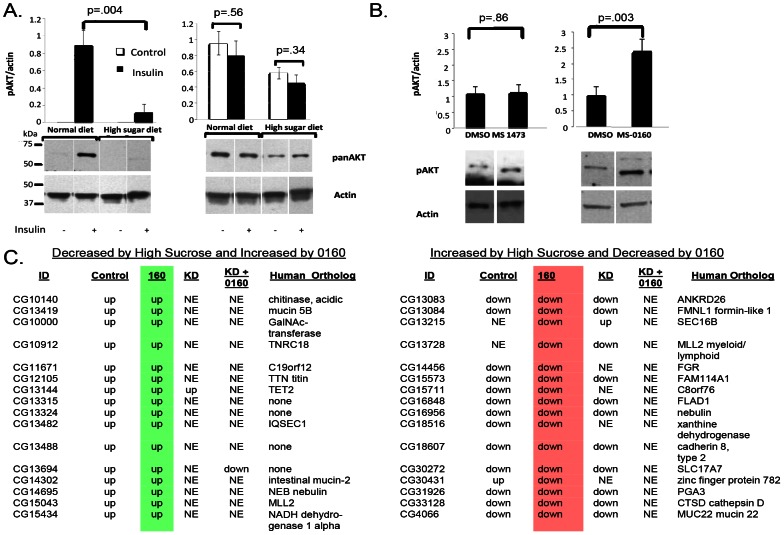
Figure 7. Insulin sensitizer effects in wild type and knockdown flies.
(A) Acute insulin action was measured in inverted larvae in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 2 µM recombinant insulin. The larvae were either grown under control conditions (left) or in the presence of high sucrose (right). Representative Western blots are shown below and the calculated areas are shown above for pAKT (left side) or total AKT (right side) normalized to actin in the absence (open bars) or presence of insulin (upper bars). An unpaired, two-tailed t-test was used to derive p-values. Error bars are ± SE (N = 3). (B) Effect of incubation with DMSO, MSDC-1473 or MSDC-0160 on the amount of insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of AKT under the high sucrose conditions (detected and analyzed as in A; mean and SE, N = 3). (C) Wild-type female flies or flies with knockdown of CG14290 (as in Figure 5) were raised on a 0.75M sucrose matrix and aged for 7 days with or without MSDC-0160 added to the matrix. RNA from flies grown under these conditions was extracted and full genome expression analysis was performed using the Agilent system. Conditions in the presence of the high sugar included control flies in addition to knock down of CG14290 (line 15858). MSDC-0160 was provided to either control or line 15859 knockdown flies. The data shown reflect changes that were more than 1.5 fold different and t-test value <9E-03 relative to the high sucrose DMSO control in terms of increase (green) or decrease (red). The list of genes, along with the mammalian ortholog names, are shown on the left in the case of where the expression was decreased in the presence of high sucrose and thus increased with the treatment of MSDC-0160 and on the right for the transcripts that were increased in the presence of high sucrose and thus reduced with the treatment with MSDC-0160. All MSDC-0160-induced changes were lost in the knockdown strain.