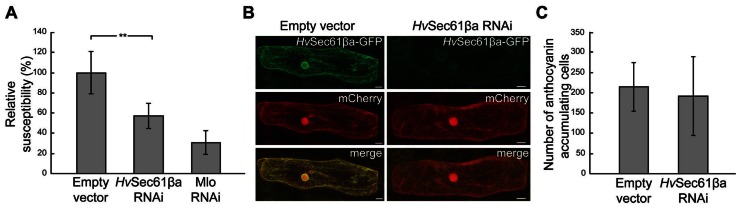
FIGURE 1.
Silencing of HvSec61βa reduces susceptibility to Bgh without affecting plant cell viability. (A) Susceptibility after co-transformation of empty vector control, HvSec61βa-RNAi and Mlo-RNAi constructs with a GUS-reporter construct into barley epidermal cells, followed by inoculation with Bgh 3 days later. The relative susceptibility was calculated as described in Materials and Methods. Mlo-RNAi was used as a positive control. Error bars represent standard deviation (SD). **, P < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). (B) HvSec61βa-RNAi reduced the GFP signal originating from HvSec61βa-GFP, but not the fluorescence signal from cytosolic mCherry 5 days after transformation. Micrographs show maximum intensity projections. (C) Number of pBC17-transformed cells accumulating anthocyanin, reflecting cell viability, after co-bombardment with either an empty vector control or the HvSec61βa-RNAi construct on similarly sized pieces of leaf. Two days after bombardment, leaves were inoculated with Bgh, and the number of anthocyanin-accumulating cells was scored 3 days later (n = 4).