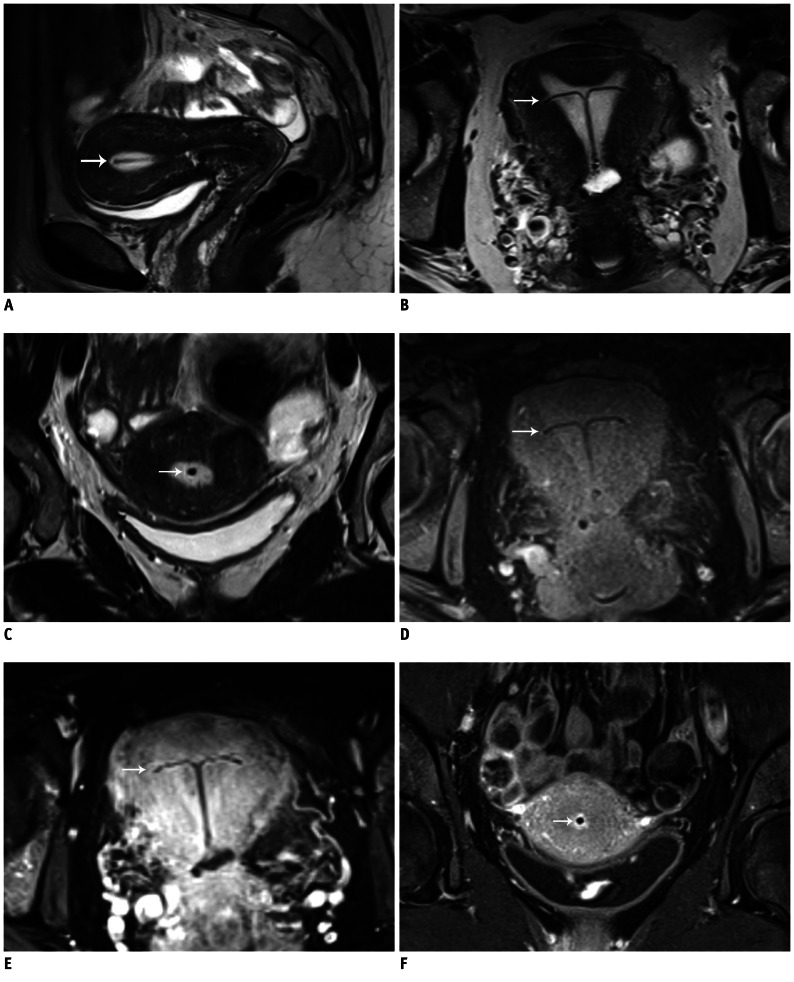
Fig. 2.
MR imaging of IUD.
A-C. Images of uterus of 42-year-old woman with undefined abdominal inflammatory disease. Sagittal (A), axial (B), and coronal (C) T2W images. IUD in fluid-filled hyperintense cavum uteri is clearly detectable without susceptibility artifacts. D. Axial T1W image. Contrast between fluid-filled cavum uteri, endo-/myometrium, and IUD is not as pronounced as in T2W images; however, IUD is clearly definable. E, F. Axial (E) and coronal (F) fat-saturated T1W images with CA (gadolinium). High contrast between hyperintense cavum uteri and endo-/myometrium and hypointense IUD. White arrow is pointing to copper-containing IUD located in cavum uteri. IUD = intrauterine device, T1W = T1-weighted, T2W = T2-weighted, CA = contrast agent