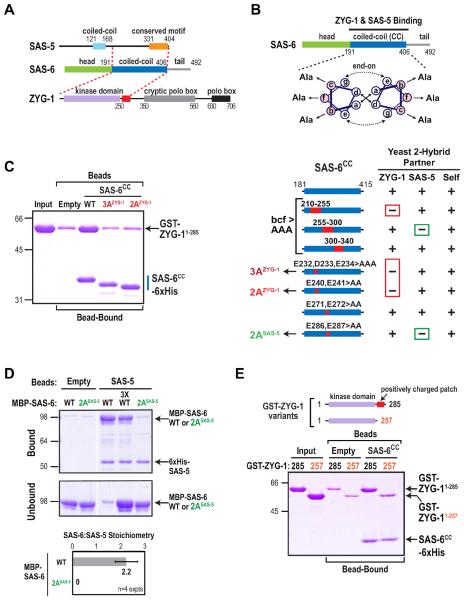
Figure 4. Engineering specific mutations that disrupt direct interactions of adjacent regions of the SAS-6 coiled-coil with ZYG-1 and SAS-5.
(A) Summary of yeast two-hybrid interactions between SAS-6, ZYG-1 and SAS-5. The SAS-6 coiled-coil interacts with the C-terminus of SAS-5 (Leidel et al., 2005; Boxem et al., 2008) and the N-terminus of ZYG-1, which includes its kinase domain and an adjacent region enriched in positively charged residues (red box). (B) (top) Schematic of the method used to identify specific residues in the SAS-6 coiled-coil required for ZYG-1 and SAS-5 binding. Depicted are hydrophobic interactions between a and d position residues (solid arrows) and electrostatic interactions between e and g position residues (dashed arrows). Charged residues in the b, c and f positions were mutated to alanine (Ala). (bottom) Summary of mutational two-hybrid analysis of the SAS-6 coiled-coil. (C–E) Purified protein pull-down assays with the indicated protein-coated beads and soluble input partners. Coomassie-stained gels of the binding assays are shown. Migration of the 3AZYG-1 and 2AZYG-1 mutant SAS-6 coiled-coils in C is accelerated relative to WT likely because the mutations render the proteins less acidic. Under the conditions used, SAS-5-coated beads saturated with SAS-6 at a SAS-6:SAS-5 stoichiometry of 2:1. The stoichiometry was calculated using molecular weight-corrected background-subtracted Coomassie staining intensities (D; bottom panel). Error bars are the SD. See also Figure S4.