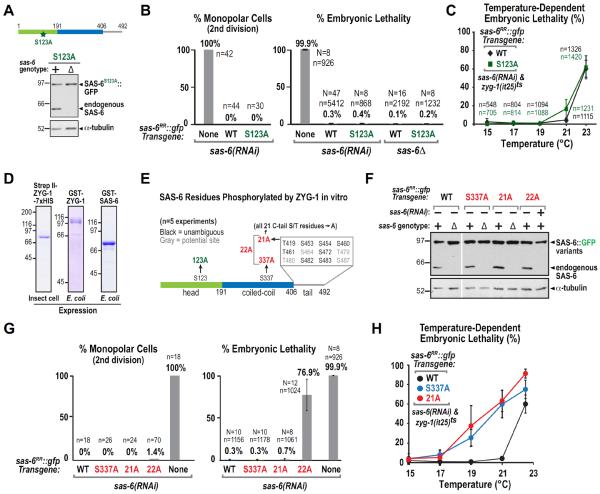
Figure 6. Neither serine 123 nor the predominant in vitro ZYG-1 target sites in the SAS-6 C-Tail are essential for centriole assembly.
(A) Immunoblot of lysates prepared from worms expressing S123A SAS-6∷GFP in wild-type (+) or in the background of an sas-6 deletion (Δ); the blot was probed for SAS-6 (top) and α-tubulin (bottom). (B) Plots of the frequency of monopolar second division (left) and percent embryonic lethality (right) as in Fig. 1H, for the indicated conditions. The WT and No Transgene data are replotted from Fig. 1H. (C) Temperature-dependent embryonic lethality of strains carrying the WT or S123A sas-6∷gfp transgenes and homozygous for the temperature-sensitive zyg-1(it25) allele. (D) Coomassie-stained gels of purified tagged ZYG-1 and SAS-6 used for the in vitro phosphorylation analysis summarized in E. (E) Summary of ZYG-1–phosphorylated sites in SAS-6, identified by mass spectrometry in at least 2 of 5 separate experiments. Mutations engineered to test contributions of these sites to total SAS-6 phosphorylation in vitro or to centriole assembly in vivo are marked in red. Sites in grey could not be unambiguously identified due to the presence of multiple serines/threonines in one peptide. (F) Immunoblots of lysates prepared from worms expressing the indicated SAS-6 variants in the presence of the sas-6 deletion (Δ) or sas-6(RNAi), as indicated; blots were probed for SAS-6 (top) and α-tubulin (bottom). (G) Plots of frequency of monopolar second division (left) and percent embryonic lethality (right), as in Fig. 1H, for the indicated conditions. The No Transgene embryonic lethality data is replotted from Fig. 1H. (H) Temperature-dependent embryonic lethality of strains carrying the S337A or 21A sas-6∷gfp transgenes and homozygous for the temperature-sensitive zyg-1(it25) allele. WT data is reproduced from C. See also Figure S6.