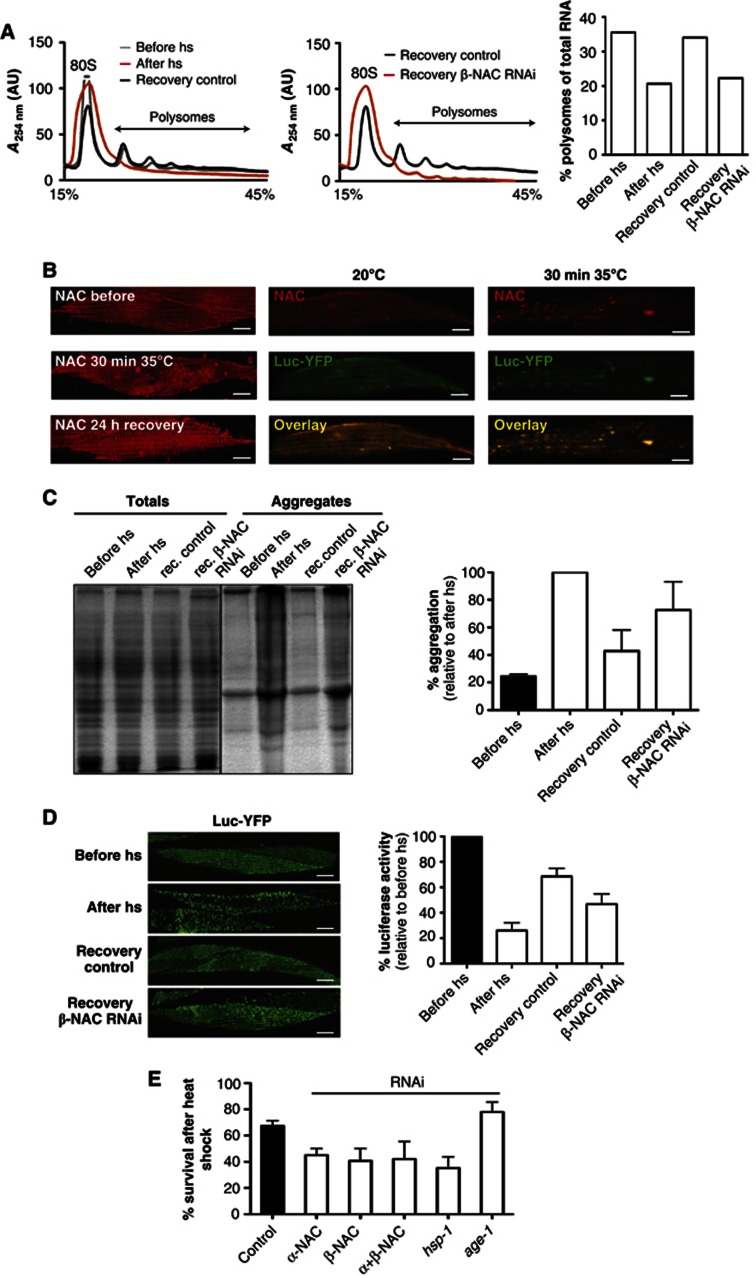
Figure 4.
NAC is important for the recovery from heat shock. (A) Heat shock of day 2 old C. elegans at 35°C for 1 h results in a reduction of polysomes (red). The condition before the heat shock (grey) and animals recovered for 24 h (black) serve as controls. The recovery from heat shock (1 h 35°C) is greatly diminished upon knockdown of βNAC (red) during the recovery period of 24 h compared to animals fed with RNAi bacteria expressing the empty vector (black; middle panel). A quantification of the polysome content with respect to the total RNA level is depicted on the right. (B) Heat shock causes reversible foci formation of NAC. Shown here is the localisation of NAC in a muscle cell of C. elegans grown at 20°C (top; left panel) and of C. elegans heat shocked for 30 min at 35°C (middle; left panel) and after 24 h recovery at 20°C (bottom; left panel). The NAC foci formed upon heat shock co-localise with aggregated luciferase-YFP. The images of the middle panel show the separate and overlay images of NAC (red) and Luc-YFP (green) at 20°C. The heat shock conditions are depicted on the right, respectively. The scale bars are 10 μm. (C) The gel shows the total (left lanes) and aggregated protein fractions (right lanes) of animals exposed to heat shock at 35°C for 1 h directly after heat shock and followed by a recovery at 20°C for 24 h upon knockdown of βNAC and of control animals, respectively. The quantification of the aggregated protein fraction of animals before heat shock (black), immediately after heat shock and animals that were fed bacteria-expressing βNAC dsRNA or the empty vector during the recovery period at 20°C for 24 h. The quantification of aggregation is normalised to the aggregation propensity after heat shock. Three independent experiments were used to calculate and draw error bars representing mean±s.d. (D) Aggregation propensity of luciferase-YFP expressing animals before heat shock (top), immediately after heat shock (second from top) and after a recovery at 20°C for 24 h in control animals (third from top) or upon knockdown of βNAC during the recovery period (bottom). The scale bars are 10 μm. An analysis of enzymatic activity of luciferase of the luciferase-YFP expressing C. elegans before heat shock, immediately after heat shock and after a recovery period upon knockdown of βNAC or in animals fed the empty vector during the recovery period are shown on the right. The luciferase activity is normalised to the enzymatic activity before heat shock (black column). Three independent experiments were used to calculate and draw error bars representing mean±s.d. (E) Knockdown of NAC reduces survival after heat shock. Animals grown on RNAi plates since L1 were subjected on day 4 to 6 h of heat-shock at 35°C followed by a recovery period at 20°C for 24 h. Survivors were scored after the 24 h recovery phase in three independent experiments with a total number of 120 animals for each condition. Error bars represent mean±s.d. of the three independent experiments.