Figure 1.
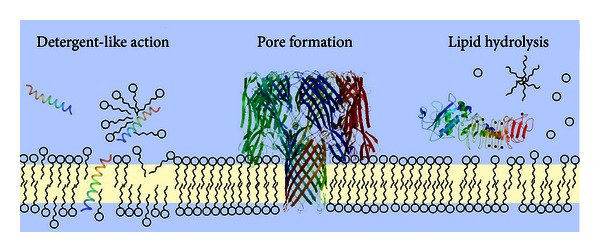
Ways to damage a lipid membrane. There are various mechanisms of membrane damage by protein toxins. Amphiphilic toxins can integrate into the membrane and essentially solubilise the lipid membrane like a detergent (structure: S. aureus δ-toxin, PDB ID 2KAM). Similarly, the membrane lipids can be hydrolysed by phospholipases also resulting in the destruction of the membrane (structure: Clostridium, perfringens α-toxin, PDB ID 1KHO, [165]). By far the largest class of membrane damaging toxins is that of the pore-forming toxins (structure: α-toxin from S. aureus, PDB ID 7AHL, [100]). These toxins integrate as stable channels into the lipid bilayer, thus creating an aqueous connection between the cytosol and the extracellular space of the target cell.
