Figure 5.
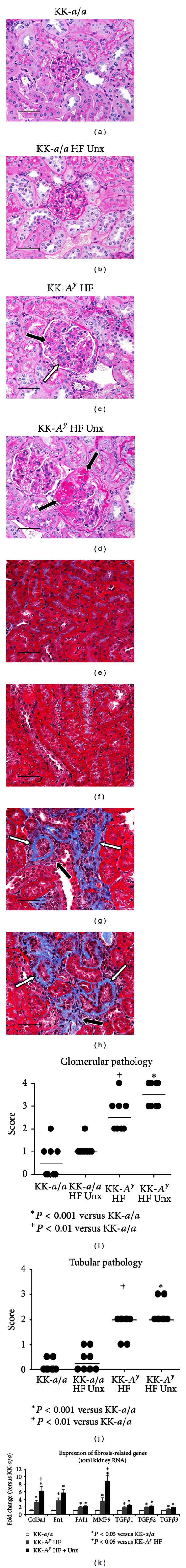
Glomerular injury in KK-A y diabetic mice. PAS staining in KK-a/a (a) and KK-a/a + Unx (b) mice revealed normal glomeruli. KK-A y mice (c) exhibited glomerular hypercellularity (white arrow) and mesangial matrix expansion (black arrow). KK-A y + Unx (d) had more severe glomerular mesangial matrix expansion (black arrow). Trichrome staining revealed normal tubules and interstitium in KK-a/a (e) and KK-a/a + Unx (f), whereas KK-A y (g) and KK-A y + Unx (h) had multifocal tubular atrophy with thickened basement membranes (white arrows) and mild interstitial fibrosis (black arrows). Scale bars represent 50 μm. (i) In the semiquantitative pathological scoring, horizontal bars indicate group median score. The binephric KK-A y diabetic mice had a significantly greater group median score for glomerular pathology (P < 0.01 versus KK-a/a controls), with a trend toward exacerbation of pathology by uninephrectomy in the KK-A y + Unx group (P < 0.001 versus KK-a/a controls). (j) Both KK-A y groups had a significant increase in tubular pathology relative to KK-a/a controls (P < 0.01 KK-A y; P < 0.001 KK-A y + Unx). (k) Whole kidney qRT-PCR indicated increased expression of fibrosis related genes by uninephrectomy in KK-A y versus KK-a/a. Expression of mRNA encoding Collagen 3a1 (Col3a1), fibronectin (FN1), serpine-1 (PAI-1), matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP9), and the transforming growth factor beta-proteins (TGFβ) 1–3 was significantly elevated in KK-A y versus KK-a/a. Addition of Unx to KK-A ysignificantly elevated expression of Col3a and MMP9 versus KK-A y(P < 0.01).
