Figure 4.
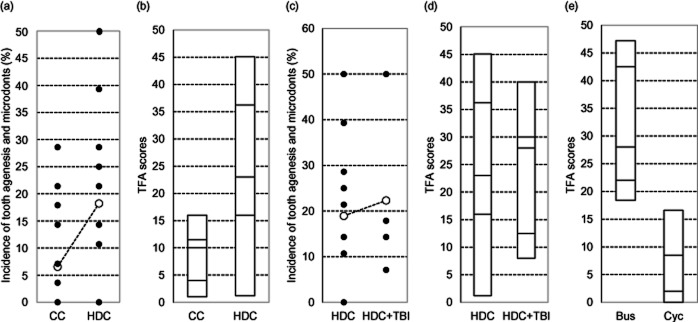
Comparison of tooth formation anomalies among subjects with conventional chemotherapy or high-dose chemotherapy with/without total body irradiation. (a) Comparison of the incidence of tooth agenesis and microdonts between the conventional chemotherapy (CC) and CC + high-dose chemotherapy without total body irradiation (HDC) groups. In subjects who started CC or were administered the 1st high-dose chemotherapy below eight years of age, the incidence of tooth agenesis and microdonts was significantly higher (P < 0.05) in the HDC group (n = 10) than in the CC group (n = 24). Open dots express medians. (b) Comparison of scores of tooth formation anomalies (TFA) between the CC and HDC groups. TFA scores were significantly higher in the HDC group (n = 14) than in the CC group (n = 26) (P < 0.01). Lines in bars express TFA scores at the 10th, 25th, 50th (median), 75th, and 90th percentiles. (c) Comparison of the incidence of tooth agenesis and microdonts between the HDC and HDC + total body irradiation (TBI) groups. In subjects who were administered the 1st high-dose chemotherapy below 8 years of age, the incidence of tooth agenesis and microdonts was not significantly different between the HDC (n = 10) and HDC with TBI (n = 4) groups. Open dots express median. (d) Comparison of TFA scores between the HDC and HDC + TBI groups. TFA scores were not significantly different between the HDC (n = 14) and HDC with TBI (n = 6) groups. Lines in the bars express TFA scores at the 10th, 25th, 50th (median), 75th, and 90th percentiles. (e) Comparison of TFA scores between the busulfan and cyclophosphamide-treated subjects. In the HDC group, TFA scores were significantly higher in the busulfan (Bus)-administrated subjects (n = 7) than in the cyclophosphamide (Cyc)-administrated subjects (n = 4) (P < 0.05). Lines in bars express TFA scores at the 10th, 25th, 50th (median), 75th, and 90th percentiles.
